Overview of the theory
This theory was developed by Lyman Porter and Edward Lawler in the year 1968 and also goes by the name Porter Lawler model that was created as an extended version of Vroom’s expectancy theory. The theorist states that there is a direct relationship between the satisfaction of an individual with his or her performance. The motive of this theory was to explain the relationship between the job attitude of an individual and job performance.
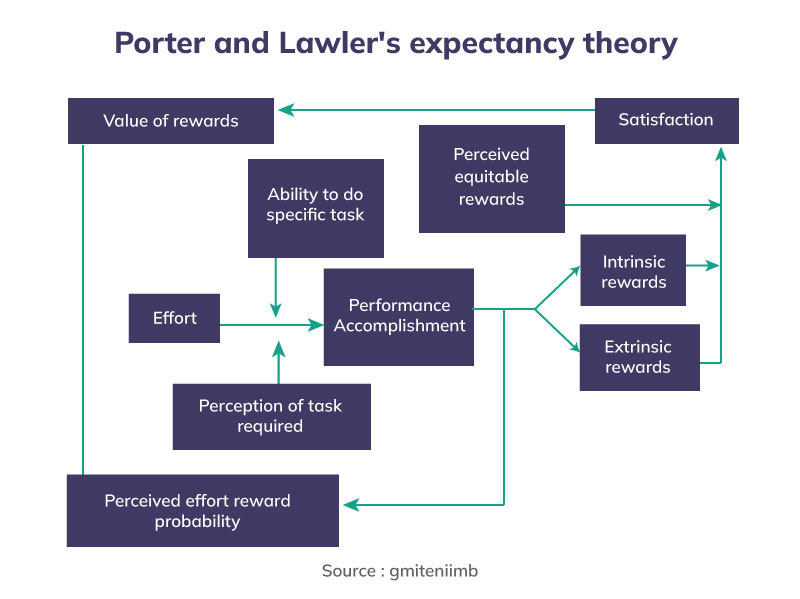
Table of Contents
The following hypotheses were proposed by Porter and Lawler
1. The behavior of an individual in an organization is based on the combination of two factors
- Intrapersonal factors include personality, and the urge to learn and adapt
- External or environmental factors include the working culture, team members, structure, etc.
2. Individuals in an organization always believe in taking rational decisions about their behavior in the organization.
3. Every individual has different goals, desires, and needs based on their culture, lifestyle, or personal preferences.
4. The expectations of individuals are a major influencer of their behavior in an organization that leads to the desired outcomes. To elaborate, it means if your expectations from an organization are low, then the efforts will be low as well which can directly affect the outcome or performance of the individual.
Probing further, below mentioned are the various elements that comprise together to create this effective model that is utilized in the contemporary world as well.
1. Effort- Efforts are an input variable that represents the energy or the amount of dedication and individual asserts in completing a task or in doing a job.
2. Value of the reward- While completing a particular task, an individual always keeps the value of the reward in mind which affects the efforts of an individual. For example, If the reward holds a major value in the life of an individual then the efforts of the person will also be multiplied. In the Vroom Expectancy Theory, this element is referred to as Valence. In addition, the theory states that every individual values every reward differently which is based on their needs and personal preferences.
3. Perceived effort-reward probability- Before putting effort into any task an individual tries to calculate the amount of effort that is required to complete the assigned task. Based on the calculated probability of efforts and the value of the reward, individuals decide the level of effort to be invested in a task or job.
4. Reward- As per the theory, there are two types of rewards awarded to an individual: Extrinsic rewards and intrinsic rewards.
- Extrinsic rewards- These include tangible or visible rewards to an individual by someone else for effective performance in the provided task. For example, Salary hikes, vouchers, or gifts.
- Intrinsic rewards- These are the interpersonal feelings of an individual that provides satisfaction to an individual on effective performance and are called intrinsic rewards. Feelings of personal growth or accomplishment in a job are some of the instances of intrinsic rewards.
5. Performance- As mentioned above, the performance of an individual is directly linked to the effort invested by the individual. Adding further, the performance of an individual is influenced by two factors
- The ability of the individual- Ability refers to the skill, knowledge, and intellectuality of an individual in performing a task or job. The ability of the person decides the efficiency of the performance.
- Individual‘s perception of the assigned role- Thinking of the individual related to their job or task directly impacts the performance. To elaborate, if an employee feels that their role in the organization is insignificant in the organization. As a consequence, the performance of an individual will be gradually affected negatively.
6. Satisfaction- Based on the perceived effort-reward probability, the individuals decide their satisfaction and dissatisfaction level with the performance. If the reward probability matches the given reward, then the employee gets satisfied otherwise dissatisfaction follows.
Implementation of the theory in a workplace
Carrying forward, the next section sheds light on how this theory can be implemented and can help employers to motivate employees at the workplace.
1. Recognizing the need for rewards
As discussed above, every employee has a different value for different rewards. Some value monetary benefits more while others focus on gaining reputation and power in the organization. Hence, the first step of implementing this theory in a workplace will include recognizing the need for rewards for every employee working in the organization.
2. Setting clear expectations
Stating up clear expectations to the employees will help managers in clearing employees' perceptions about their role and importance in the organization.
3. Make performance evaluations fair and transparent
It is essential for employers to evaluate the performance of the employees fairly and with transparency. So that the employees can trust the decision-maker and invest their efforts accordingly.
4. Assigning tasks to the employees based on their ability
Every individual has a different skill set and different intellectual approach to performing a task. Managers can assign different tasks to different people based on their abilities.
Moving ahead, this theory holds major importance in the contemporary world and can help in multiple ways. Hence, the next section highlights the importance of implementing the theory in the workplace.
Importance of implementing this theory in a workplace
- Matching the ability of an employee with an assigned task will assist employers to get the best possible outcomes from the team that will help in growing the organization.
- Realization of the role and importance of an employee in the organization can assist employers to motivate employees to give their all in the organization.
- Identifying and giving the right reward for an individual can motivate him or her to perform more efficiently to get the desired outcomes.
However, below mentioned are the limitations of this theory that should be considered while implementing this theory in the organization.
Limitations of the theory
- Neglected the impact of feelings on motivation - The theory’s main focus was on how motivation is the main driver of performance. However, the theory failed to state how the feelings and external problems of an individual can affect the motivation of the employees.
- Motivation limited to rewards - In the theory, Lyman Porter and Edward Lawler only focused on monetary and non-monetary rewards to influence the employees’ motivation. However, the theory did not acknowledge other factors such as working environment, relationship with colleagues, or working culture that can affect the motivation of an employee and thus the performance of the team as well.
Probing further, below mentioned is an example of implementation of the theory that will help in comprehending the theory in the most effective way.
Example of implementing the theory in the workplace
Jack wanted to start a new venture under the name of the same company and wanted assistance from two of his employees (Megan Stein and Ashley Adkison) to assist in building the portfolio of the company from scratch. However, Jack knew that both of the employees were not interested in helping him in exchange for any reward. Hence, he decided to apply Porter and Lawler's expectancy theory in order to motivate employees.
- 1. The first and the foremost step that was taken by Jack was to call both the employees and explain the amount of effort that was required by both of the employees in performing the task efficiently.
- Next, knowing the importance of the value of the reward, Jack asked Megan and Harry about the rewards they would wish to receive on completion of the task.
- Megan demanded an increment in the current salary package that falls under the category of extrinsic reward.
- On the other hand, Harry asked for a promotion that would give him a feeling of accomplishment and this reward was under the category of intrinsic rewards.
- Jack agreed to the terms of both the individuals to get them on board. The next step taken by Jack was to assign the task to Megan and Harry based on their abilities. Harry was good with HR management so he was assigned the duty of recruiting the new team. On the other hand, Megan was good with technology, so she became in charge of taking care of all the technical aspects of the new venture.
- After assigning the task, Jack explained the value of the contribution of both the employees and assigned duties according to the specialization that assisted both the employees in giving their best.
- After completion of the task, Jack kept the word and provided Megan with the hike in the salary and Harry with the promotion. After getting the desired award, both the employees were satisfied.
Key takeaway - Theory assisted Jack in getting the desired work done from both the employees and with the desire of earning a favorable reward, both the employees delivered the work in the most efficient manner.
FAQs
Can the same rewards be equally motivating for all employees?
No, the same rewards may not be equally motivating for all employees. Different individuals have different preferences and priorities, and what is highly valued by one employee may not be as attractive to another. Organizations should consider individual differences when designing reward systems.
Can the Expectancy Theory explain why some employees are not motivated despite having high skill levels?
Yes, the Expectancy Theory can explain this phenomenon. If an employee lacks confidence in their ability to perform well (low expectancy) or believes that even successful performance will not lead to meaningful rewards (low instrumentality), their motivation may be low, regardless of their skill levels.
Pervious Theory
Alderfer’s ERG TheoryNext Theory
McClelland’s Theory
 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register