Overview of the theory
Clayton Paul Alderfer developed a theory that was another version of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory in 1969. In his model, he stated that there are three factors that dictate human behavior in society. To elaborate, ERG in the name of the theory stands for Existence, Relatedness, and Growth. The most important and basic of all the three categories are the needs for existence and the rarest yet the most important is the last category i.e. the needs for growth. In this theory, Alderfer states that human priorities are not constant and they can change from time to time according to the mood and personal requirements of an individual.
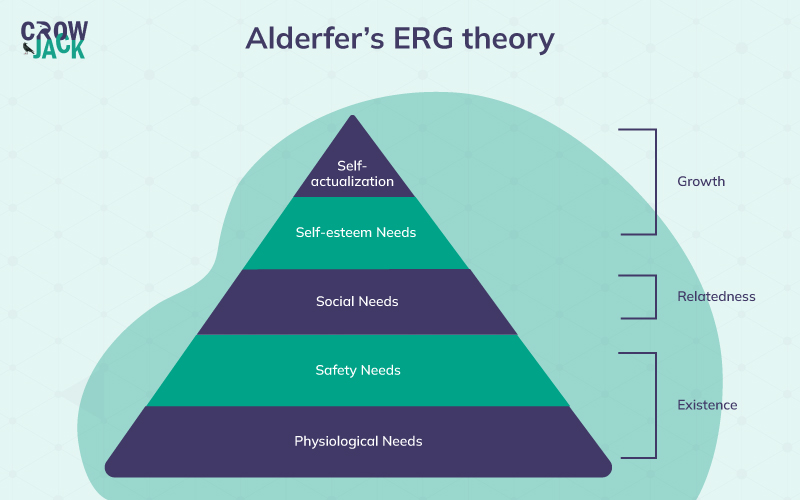
Further elaborating, below given are the three categories of human motivation stated by the theorist
Table of Contents
- Existence - This section includes all the needs that are the most important for the survival of human beings. In reference to Maslow's hierarchy of needs, existence needs are the combination of physiological needs and safety needs. Basic necessities like food, shelter, security, mental health stability, and sleep are included in this category. In addition, Alderfer's also included the needs of employment and health under this category.
- Relatedness - Similar to Moslow’s social or love and belonging needs, Alderfer states that interpersonal relationships are crucial for human survival and included all the relationships in the relatedness category. This category includes basic healthy interactions with family, friends, or colleagues around them.
- Growth - Alderfer summed up Maslow's self-esteem and self-actualization needs under the category of growth. This rarely achievable stage includes the personal growth and development of an individual. At this stage, humans focus on achieving the best version of him/herself.
Further, the theory explains the relationship between frustration and regression and names it the ‘Frustration Regression Principle’ which states that whenever a human fails to achieve a higher level then he or she may frustratedly regress to the lower levels that may seem easy to excel.
Probing further, the next section draws attention to the comparison between Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs and Alderfer’s ERG theory.
Comparison between Alderfer’s ERG theory and Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- According to Maslow’s theory, attainment of one level of needs is necessary to reach the next level. For example, fulfillment of physiological needs is necessary to reach the level of safety needs.
On the contrary, Alderfer states that it isn’t necessary that humans need to fulfill the previous stage in order to attain the next one. For instance, a person can focus on personal growth first, rather than improving social relations with other humans.
- In Maslow’s theory, humans always follow the upward approach in the pyramid to reach the top level in order to fulfill all their needs.
Contradicting the same, ERG theory states that it is not necessary that humans need to follow the order to satisfy human needs. For instance, If a person is unsuccessful in fulfilling the needs of existence, then he can easily move ahead with relatedness or growth needs.
Moving ahead, every theory has its way of implications and holds separate importance in implementing the theory in a workplace. Therefore, below are the ways in which Alderfer’s ERG theory can be implemented in a workplace.
Implementation of the theory in a workplace
1. Identify unsatisfied needs at the workplace
The first and the most crucial step is identifying the factors and needs that are affecting the motivation of employees negatively. Multiple methods of taking feedback or analyzing the work environment can be taken into consideration while identifying the unsatisfied needs.
A few questions that can help in identifying the unsatisfied needs are mentioned below
Existence
- Are working conditions of the workplace fine?
- Are they getting reasonable wages or salaries and is the delivery of salary on time?
- Are employees getting enough time to have their meals properly?
- Do they face any kind of physical or mental stress while working in a workplace?
Relatedness
- Is the work provided enough to maintain a healthy work-life balance?
- Are employees getting time to socialize enough to fulfill their social needs?
Growth
- Are employees getting enough growth opportunities to grow?
- Is the company putting any extra effort to upskill the employees?
2. Make the required transformations
Once the required changes are listed out as per the operations of the workplace, the required and possible changes can be made to ensure a smooth workflow in the organization. All the unsatisfying needs should be fulfilled and the workplace should become more of an employee-centric organization.
3. Evaluate the after effects
The last but not the least step is to make sure whether the implied transformations are leading to positive effects in an organization or not. This can be done by conducting open discussions, asking for anonymous, or open feedback. This will help in evaluating the after-effects of implied strategies and will give a clear picture of the working environment and satisfaction of employees.
Continuing further, below mentioned are a few of the valid reasons for implementing this theory in a workplace.
Importance of implementing the theory in the workplace
- This theory assists in identifying the unsatisfactory needs of the employees that can affect the productivity of the workplace negatively and helps employers in eliminating them.
- When employees are stress-free from the attainment of basic needs, they are more focused and concentrated on work and this will assist them in giving their all to an organization.
- Focusing on the attainment of needs will help employees in becoming the best version of themselves that can assist the company in making their human capital strong and earning better profits.
- ERG theory effectively filled out some of the limitations of Maslow’s theory which gives the right to the person to choose the important needs according to their preference rather than following a pre-decided order.
Moving ahead, there are certain limitations of the theory that can be a matter of discussion while implementing these theories in the workplace.
Limitations of the theory
- No effective guiding path to follow is provided in the theory for a person to effectively choose the important need that is to be fulfilled first among the three.
- No solutions are given in the theory for the big organizations because it might be impossible for organizations with a large number of employees to analyze the individual needs of every employee.
Carrying forward, an illustration of an example of a company will assist in comprehending the theory in an efficient manner.
Example explaining the implementation of the theory
Nestlé is the world’s largest food and beverage processing conglomerate operating worldwide with headquarters in Switzerland. As of 2021, Nestlé provides employment to approximately 276,000 people around the globe. To retain such a large workforce, Nestle utilizes multiple strategies and implements various theories to motivate and engage employees in a work environment.
To validate, ERG theory is directly related to the HRM practices of Nestle and the company takes various employee motivational initiatives to fulfill the needs of the team. Nestle provides multiple well-being and development programs that assist in prioritizing and fulfilling the needs of employees to motivate them to perform better.
Existence needs - Nestle fulfilled employees’ existence needs by introducing various employee health programs such as “Know Your Numbers Programs” which provided free health checkups for the employees to identify multiple health risk factors affecting their bodies. In addition, they also provided various programs on stress and health management to assist employees in maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Relatedness - Nestle introduced the “InGenuis project” to enhance the onboarding process for the new employees to know their office location, colleagues, and other facilities and features of the company. This project assisted in fulfilling the relatedness need of the employees by giving them the opportunities to socialize and interact with coworkers and get comfortable with the company.
Growth - Under the same project Nestle also introduced InGenuis Innovation Ecosystem. In this project, the company is dedicated to creating an entrepreneurial team and a crowdsourcing platform where employees can collaborate and innovate new ideas that will assist in the growth of the company. Providing employees the platform to grow and innovate will aid the company in fulfilling thea growth needs of the employees. As of 2021, almost 83’000 Nestlé employees from around the world have generated 9750 new ideas and submitted over 128’000 votes and comments.
Key takeaway
Offering various development programs to provide growth opportunities and fulfilling the basic needs of the employees assisted in enhancing the productivity of the employees. Along with this, it also assisted employees in coming up with new ideas that can lead to their personal and company growth.
FAQs
How does Alderfer's ERG theory differ from Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
Alderfer's ERG theory compresses Maslow's five-level hierarchy into three broader categories of needs. Unlike Maslow's rigid sequence of needs, Alderfer's theory suggests that individuals can be motivated by multiple needs simultaneously, and if higher-level needs are frustrated, they may regress to pursue lower-level needs.
How does Alderfer's ERG theory contribute to understanding employee behavior and motivation?
Alderfer's ERG theory provides valuable insights into the complexity of human needs and motivation. By recognizing that employees may have multiple needs simultaneously, managers can develop more comprehensive and tailored motivational strategies to support their workforce effectively.
Pervious Theory
Theory X and Theory YNext Theory
Porter and Lawler's Theory
 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register