Overview of the theory
This theory was proposed by Victor Vroom in 1964 stating that the amount of effort invested in performing a certain action is influenced by the strength of expectations and the significance of reward for the individual.
Further, he states that there are three kinds of relationships that are formed effort, performance, reward, and goals.
Effort performance relationship
Efforts of an individual invested in the assigned task are directly related to the performance of an individual. The more effort, the better will be the performance of an individual.
Performance reward relationship
The performance will directly affect the reward that was to be received by performing the assigned task. If the performance is up to the desired mark, the possibility of receiving the reward increases.
Reward personal goal relationship
Rewards received from the organization can assist in fulfilling the personal goals of an individual. If an individual receives an award, he or she can utilize it in attaining personal goals.
Table of Contents
There are multiple factors that affect all the above-given relationships
- Comprehension of the performer regarding the relation of outcome and performance. For example - it depends on the factor that whether the performer understands clearly what he/ she will get if they perform the task very well/ That understanding will influence his motivation directly.
- Trust of the performer on the decision-maker of the reward. For instance, it matters if the employee trusts the decision made regarding the reward or not. Because lack of trust can demotivate employees to give their best.
- Degree of transparency in the decision-making process. For example, if the employers decide with minimal transparency then the other employees might doubt the credibility of the decision and might lose their trust in the employer.
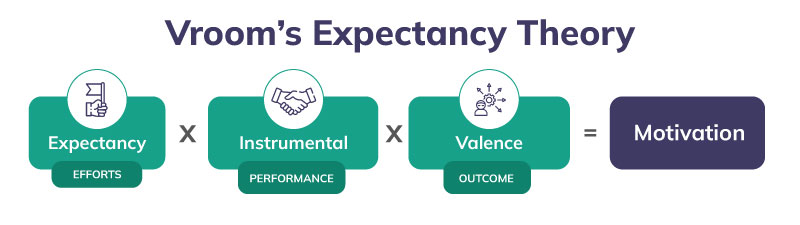
Moving ahead, the Vroom highlighted the three key variables that affect the effort, performance, and motivation of an employee in an organization.
1. Expectancy (E) - The expectation from oneself regarding the completion of a task that determines the efforts of an individual. For example, if an employee expects that they can perform the assigned task within the given deadline, then the employee will perform his or her best. In addition, it becomes an obligation of the employer as well to set achievable goals for the employees to accomplish. Expectancy is usually estimated by
- The required skills set
- Availability of the resources
- Perception of the future growth
2. Instrumentality (I) - The attainment of the promised reward is included under the category of instrumentality. The mindset of the employee is usually dependent on the Individual’s trust in the decision-maker of the reward
3. Valence (V) - Valence refers to the value of the reward awarded to a person. If the assigned reward is valuable to the employee then they will invest in better efforts. On the other hand, if the reward does not matter to the employee, employees will not try to give their best.
Based on these three key variables, there can be two possible outcomes
- Effort-performance expectancy - This refers to one’s belief that higher efforts will lead to better performances.
- Performance-outcome expectancy - In this case, an individual believes that the higher performance will assist in getting desired outcomes.
Vroom further states, that all the three listed variables are interdependent on each other and if any of the factors is missing, the motivation of an employee will be nil. He also provided the mathematical formula through which the motivation of the employee can be calculated.
Motivation(M) = Expectancy(E) x Valence (V) x Instrumentality (I)
To continue, this theory is highly applicable to the contemporary business environment because every employee is highly attracted to and motivated by the desired rewards. Hence, below mentioned are a few of the strategies that can be utilized to implement this theory in a workplace effectively.
Implementation of the theory in a workplace
1. Matching the value of effort to the reward
In order to get the desired outcome from the employees, managers should always match the value of the reward to the expected outcome. To elaborate, this means that if the task assigned is difficult, then the reward should be expensive or more valuable to the employee.
2. Building a trustworthy relationship with the team
Managers should try to build a healthy and trustworthy relationship with their teams because as discussed above, the employees' trust in the decision-maker will influence their performance.
3. Providing the promised reward
It is an obligation of the manager to provide the promised reward because this will motivate the employee to constantly keep investing the same or increase efforts in performing future tasks. If the promised reward is not awarded to the employee for better performance, it will demotivate the employee from investing efficient efforts in the next tasks.
4. Understanding the difference in needs
The needs of every employee is different from one another and employers must ensure that the awarded reward is always assigned according to the desired need of the employee. This can be done by asking the rewards from the employee they wish to receive on delivering the required performance.
5. Providing all the required resources
It is necessary to ensure that all the prerequisites to complete a certain task should be provided to the employee because this will assist in giving the employee confidence in completing the task and increasing the expectancy of the employee
Moving ahead, there are various reasons why implementing the theory in the workplace will benefit employers. Hence, listed below are some of the reasons for implementing this theory in the workplace.
Importance of implementing the theory
1. Assists in motivating employees
When the employees will get the rewards they value or desire the most, it will assist in motivating employees in adding their full potential to the assigned task in order to get the desired reward.
2. Assists in retaining employees
When employees feel that the employer is taking care of their needs and provides valuable rewards to them for fulfilling the task, this will assist in engaging the employees in a more efficient manner. In addition to this, the engaged employees will remain with the organization for a longer period of time.
3. Helps in the growth of the company
Identifying the needs and providing the rewards to the employees that they value will assist in gaining the loyalty of the employees. This will help in engaging employees and attracting the employees to give their best towards the growth of the company.
Probing further, although this theory is relevant in the contemporary workplace, it still has some limitations that must be addressed before implementing this theory.
Limitations of the theory
1. Employees can demand impractical rewards
As the theory suggests that the reward should always be provided according to the needs of employees. However, there can be certain situations when employers might not be able to fulfill the demands of the employees, or sometimes employees' demands are too irrational to be fulfilled. In these cases, the employees will remain demotivated and it will gradually affect the performance of the employee.
2. Mention of limited factors affecting expectancy
In the theory, Vroom failed to acknowledge some of the additional factors like capability, deadlines, stress, and personal problems of the employee that might affect the expectancy variable of the theory.
3. Too idealism involved in the theory
The whole theory is based on the assumption that higher efforts and high performance will directly assist in getting the desired outcomes which might not be true all the time. The influence of external factors such as work environment, support from team members, or any kind of favoritism can affect the desired outcomes of the employees.
Probing further, an example of the implication of the theory is provided to effectively demonstrate the theory.
Example of implementing the theory in a workplace
An employer has a team of 4 members in his sales team and he sets a target of completing a sale of $20,000 by the end of the month.
By keeping Vroom’s Expectancy Theory in mind, the employer decided to call a team meeting and convey all the instructions for achieving the desired goal.
- Expectancy - The employer first explained to all 4 members all possibilities of achieving the desired results and justifies setting an achievable target with the accurate amount of effort invested. In addition to this, to fulfill the need for resources, the employer-provided company phones all team members for calls along with the data of potential leads essential for making sales.
- Valence - Acknowledging the importance of valence, the employer asks all the 4 members about the reward they will wish to receive for the accomplishment of the goal. All 4 members demanded different things. The employer considered the rationality of the demands and agreed to provide them the desired reward for completing the assigned task.
- Instrumentality - Employees trusted the employer’s commitment and were successfully able to achieve the target. On the completion of the goal, the employer fulfilled the demands of all the team members and the employers were satisfied.
Key takeaway
Through the implication of the theory, the employer was able to get the task done and convinced employees to give their all to achieve the target in exchange for the desired reward.
FAQs
How does Vroom's Expectancy Theory differ from other motivation theories?
Vroom's Expectancy Theory differs from other motivation theories in its focus on cognitive processes and the individual's perception of the link between effort, performance, and rewards. Unlike some theories that emphasize the role of specific needs or intrinsic factors, Vroom's theory highlights the importance of personal expectations and evaluations of outcomes.
How can organizations apply Vroom's Expectancy Theory to enhance employee motivation?
Organizations can apply Vroom's Expectancy Theory to enhance employee motivation by ensuring clear communication of performance expectations and the relationship between performance and rewards. Providing meaningful rewards and recognition for outstanding performance can also strengthen the belief that effort leads to valued outcomes, boosting employees' motivation.
Pervious Theory
McClelland’s TheoryNext Theory
The Equity Theory
 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register