Overview of the theory
Formed in 1959 by the psychologist Fredrick Herzberg, this theory goes by multiple names such as Two Factor Theory, Herzberg’s Motivation Theory, and Dual Structure Theory. Herzberg concluded this theory by conducting interviews with almost 200 professionals from white-collar jobs asking only two questions:
- What was the moment that made them happiest at their job and why?
- What was the moment that made them feel bad about their job and why?
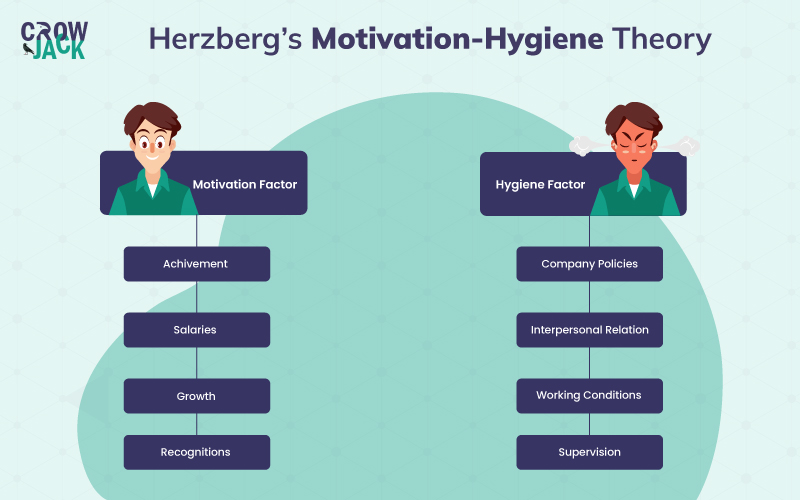
Based on the answers, he concluded that there are two major dimensions of job satisfaction: motivators and hygiene factors.
Table of Contents
1. Motivating factors
These are the factors that increase job satisfaction by motivating employees. The factors that can motivate employees in a workplace include
- Achievement - Achieving small or big goals set by the employees or employers can motivate them to work better and be more productive.
- Salary - Offering competitive salaries is always a major booster for employees to work harder for the growth of the organization.
- Growth - Exposure to multiple growth opportunities such as e-learning platforms and credentialed programs offering online badges, can enhance the motivation of employees in order to excel in their careers.
- Recognition - Appreciating the efforts of employees and giving multiple monetary or other non-monetary benefits can assist in boosting the confidence of employees and encouraging them to perform their best. To substantiate, as per Vantage Circle, more than 40 percent of employees feel demotivated and switch jobs because of lack of appreciation.
2. Hygiene factors
Hygiene factors do not play a major role in motivating employees but on the other hand, the absence of these factors can demotivate employees. To elaborate, the hygiene factors that can lead to dissatisfaction among employees are mentioned below
- Company policies - Though employees might not get motivated by company policies but bad company policies can contribute to unhealthy work culture and can demotivate employees.
- Interpersonal relationships - For some employees, lack of communication with employer or colleagues during working hours can make employees feel isolated and lonely which can further demotivate them.
- Working conditions - The place where employees' working environment can not be a direct factor of motivation, however, a lack of an appropriate working atmosphere can discourage employees from giving their full attention and concentration. Unsafe or unhygienic work conditions are among the major ethical issues in the workplace that can lead to high disengagement among employees.
- Supervision - Supervising the activities of employees is one of the obligations of managers. However, when supervisors instead of surveilling, start using the approach of micromanagement with employees, then it can disengage and demotivate employees.
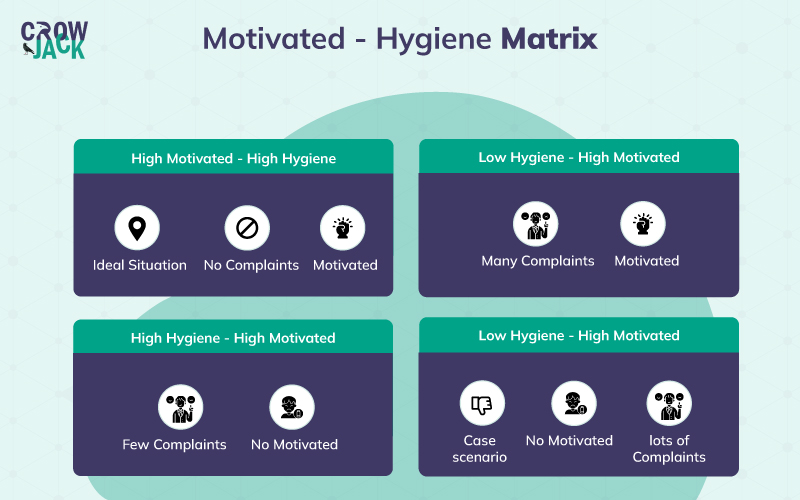
It is well understood that job satisfaction and dissatisfaction factors must be diligently evaluated. An organization providing both recognition and good working conditions will automatically lead to achieving motivational parameters that are even stated in other theories such as Porter Lawler's Theory corresponding to superior satisfaction levels and performance accomplishment. Probing further, the theory indicates that there are 4 cases also known as Motivation Hygiene Matrix in which workplace usually finds themselves
- High motivation and high hygiene - This is an ideal situation of a workplace where employees are highly satisfied with their job and have almost no complaints from their employers. For example, in a workplace, employees are very much satisfied with the company’s policy, and their salary and are getting good growth opportunities along with recognition of their efforts.
- Low motivation and high hygiene - In this situation, employees are getting a good environment to work in but do not have any motivating factors in the workplace. The instance of this situation can be related to a workplace where employees are getting good working conditions but are recruited at a low salary.
- High motivation and low hygiene - In situations where there is high motivation and low hygiene, employees work for the exposure but do not get a suitable working environment or are not satisfied with the company policies or other colleagues. For instance, there is a workplace where there are many good growth opportunities but the infrastructure or the working environment of the office is not appropriate enough.
- Low motivation and low hygiene - This is the worst possible scenario that can occur in a workplace, in these situations employees are neither motivated nor are satisfied with the working culture of the company. For example, in a workplace where there are no recognitions or promotions and employers practice the approach of micromanagement.
Moving ahead, there are a few steps that can be taken into consideration while implementing Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene model in the workplace.
Implementation of the theory in a workplace
1. Identifying the stressors and motivators
The first and foremost step is to analyze the workplace which will assist in identifying the factors that can affect the job satisfaction of the employees. This can be done by either observing or by directly interacting with the employees and taking required feedback.
2. Eradicating the factors that encourage job dissatisfaction
After identifying the factors, it is necessary to list out the motivating and demotivating factors. After listing out, all the necessary actions should be taken to eliminate the factors that lead to dissatisfaction among employees.
3. Boosting the factors that motivate employees
The next step is to boost motivating factors that will encourage the level of satisfaction of the employees. This will assist in motivating the employees and will also affect the productivity and performance of the employees positively. For instance, a well laid down DEI policy can significantly boost workplace motivation in a diverse workforce.
Delving deeper, after understanding the theory thoroughly, the next segment focuses on the importance of implementing this theory in the workplace.
Importance of implementing the theory in a workplace
1. Better work environment
If the factors are identified and eradicated efficiently, then it can help in boosting the motivation of employees and bring positiveness to the environment making the work environment better and more efficient.
2. Enhanced motivation
When employees get a suitable working environment along with the motivating factors, it can assist in boosting the motivation of the employees to work with more dedication for the betterment of the company.
3. Identifies Unsatisfactory needs
This theory assists in identifying the unsatisfactory needs of the employees because a majority of the employers consider that money is enough to satisfy the needs of employees. However, this theory draws our attention to the multiple factors that can influence the motivation of the employees negatively or positively.
Probing further, this theory also came up with some of the limitations that failed to fill the gap in the model
Limitations of the theory
1. Deficit of contextual variables
The biggest limitation of this theory was the lack of situational variables. To elaborate, this theory mainly focuses on a non-variable structure that has a limited number of motivating and hygiene factors for a certain workplace situation. To elaborate, in the theory, Herzberg only covered 200 professionals from white-collar jobs and there are chances that in some workplaces, the motivators and hygiene factors are opposite to the theory. For instance, for some employees, salary might not be a motivator but a healthy working environment can be. Therefore, this theory lacked the mention of situational variables.
2. Ignorance of external factors
Another limitation of this motivational theory is that there is no mention of how external factors like competitors or other microenvironment factors can influence the working decision of employees within an organization. For example, an employee working at a local company gets an opportunity to work with a multinational company. In that case, it will not matter how good the maintenance of motivating factors in the local organization is, the employee will not be satisfied with the old job. Hence, external factors are as important as internal factors of the organization and Herzberg did not cover the external factors affecting the motivation of the employees.
3. Based on subjectivity
Another limitation of the theory that is worth mentioning is that the theory is based on subjectivity. The theory was formed on the 2 basic questions that might have been fabricated or influenced the results. Along with this, every person has a different definition of satisfaction, and measuring satisfaction with the happiest and saddest moments at the job might not be an appropriate measure for many employees. Thus, this theory was more based on subjectivity which might have encouraged biases in the results.
4. Productivity may not be directly linked with satisfaction in some cases
One of the other biggest disadvantages of this theory is that Herzberg directly linked satisfaction with the productivity of employees which might not be always true. Though the satisfaction of employees can lead to more productivity, it may not be the case every time. For example, an employee gets satisfaction by delaying the work and because of the lenient work environment, he gets that satisfaction by delaying work. This implies that even after the fulfillment of satisfaction needs, the employee is not productive.
Relating this theory with a hypothetical example of a company will give us a clear comprehension of the theory that can assist in making an organization a better place to work.
Example explaining the implementation of the theory
Amazon, one of the biggest multinational technology companies around the globe, is working day and night to become Earth’s most customer-centric company, Earth’s best employer, and Earth’s safest place to work. To achieve the goal of becoming the Earth’s best employer, Amazon believes in taking care of its employees and they accomplish this by implementing various theories to keep them motivated and hyped to work for the betterment of the company. To validate, let’s look at one of the examples of implications of the theory of motivation at Amazon.
The manager in one of the offices of Amazon, Shawn, suddenly realizes that there are certain factors in the organization that highly motivate and demotivate his employees during working hours. However, Shawn was not able to identify the key factors that were affecting the employees positively as well as negatively.
To continue, Shawn decided to implement Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory in order to identify the motivating and hygienic factors that were impacting the workplace. To elaborate, Shawn decided to take anonymous feedback from the employees, so that employees can write honestly without hesitation or with the fear of upper management. After analyzing, Shawn identifies employee engagement activities and employee of the month as the major motivating factors and noisy environment due to some employees and micromanagement of a few project managers as the hygiene factors affecting employee motivation negatively.
After identifying hygiene factors, the employer decides to implement a strict regulation with serious consequences for those creating noise during working hours. Along with this Shawn introduced a few workplace policies in which clear instruction on avoiding micromanagement was implied and even conveyed project managers personally to focus on the results and not the process.
In the case of motivating factors, Shawn for the list of rational gifts that employees might wish to have if they get chosen as an employee of the month. So, it can boost the motivation of employees to work better to get the desired gift.
In addition to the same, the manager decided to enhance the number of employee engagement activities and decided to conduct the activities every Saturday for the employees to get more engaged and get enough time to relax and remain stress-free from work.
Key takeaway - Applying the theory in the workplace assisted the manager of Amazon to eliminate all the unsatisfactory factors that demotivate employees in a workplace. Furthermore, it assisted Shawn in identifying and boosting the motivating factors that assisted in enhancing the productivity of the employees.
FAQs
How does Herzberg's theory differ from other motivation theories?
Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene Theory is different from traditional content theories (e.g., Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs) as it focuses on two separate sets of factors: motivators and hygiene factors. It also differs from the expectancy theory, which emphasizes the relationship between effort, performance, and rewards.
Can a job with adequate hygiene factors still have dissatisfied employees?
Yes, even if hygiene factors are met (e.g., fair pay and good working conditions), employees may still be dissatisfied if the job lacks meaningful tasks or opportunities for growth and recognition. In such cases, the absence of motivators can lead to reduced overall motivation and satisfaction.
Previous Theory
Maslow’s theoryNext Theory
Theory X and Theory Y
 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register