Overview
The participative style of leadership, also often called the democratic style of leadership, was popularized by Kurt Lewins between the 1930s and 1940s. He highlighted the significance and the positive implications of participative leadership within an organization.
So let's get started by discussing what is the participative theory. To substantiate, the participative style of leadership proposes a leadership style that includes all employees or members of an organization in the decision-making process. As the term participative suggests, the theory speaks in favor of everyone’s participation when it comes to valuable and crucial decisions for the overall success of an organization. The central idea around which this leadership style revolves is collective input coming from all members. Having said that, leaders encourage their employees or followers to share their ideas and opinions without any reluctance.
Probing further, it is essential to note that participative leadership can be further classified into four sub-categories that are listed below.
Table of Contents
Types of participative leadership
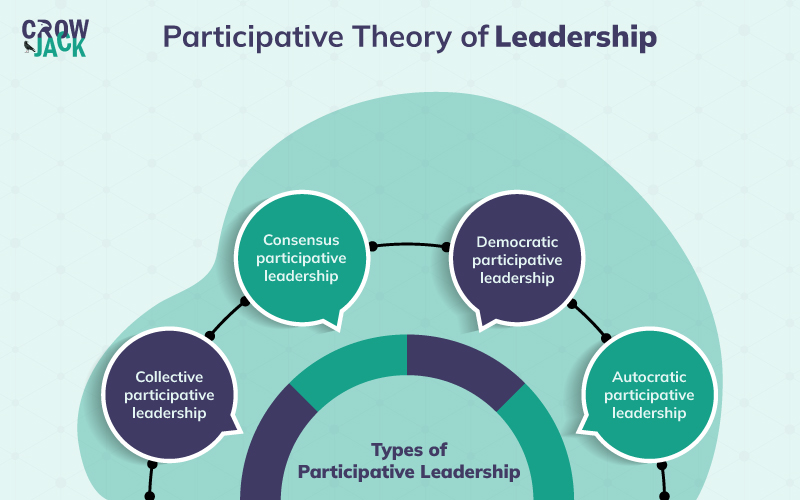
1. Collective participative leadership
In this style of participative leadership, the organization or group has collective responsibility with respect to the outcome. The leaders surely facilitate the processes and guide the way but the accountability is collective. Also, when it comes to decision-making, the majority number of employees or members should agree to proposed decisions with respect to change management.
2. Consensus participative leadership
In this style, leaders do not assume any undue power advantage over other members. They simply work as a facilitator and seek the consensus of the entire team to reach decisions. The key difference between collective participation and consensus participation is that in the latter, all members must agree to the proposed decisions or strategies.
3. Democratic participative leadership
In the democratic style of leadership, the leader seeks opinions and inputs from all members of the team but the final discretion lies with the leader. In simpler terms, the leader has much more influence and power as compared to the collective influence of members. Even if there are voting procedures, the leaders have the final say.
4. Autocratic participative leadership
In autocratic participative leadership, leaders assume even greater power than in the case of democratic participative leadership. Although opinions and ideas are sought from members to engage their participation in the process, little preference is given to members’ ideas in contrast to the leader’s recommendations.
There are different levels of indulgence in decision making subject to different organizational structures. Now that we have evaluated the four different contexts of participative leadership, let us underline some salient features of the participative theory of leadership as a whole.
Key features of Participative Leadership Theory
There is great emphasis on open communication within teams and members have the freedom to express their views, opinions, and perspectives to add value to the organization. This further leads to greater workplace motivation.
The participative style of leadership inspires great unity among teams and employees feel valued in the sense that their suggestions are accepted wholeheartedly by leaders. Having said that, strong unity acts as the perfect foundation for incredible outcomes.
Because of different perspectives coming into the picture, the decision-making is not only inclusive but highly optimized as the pros and cons of all opinions are assessed individually.
Participative leaders have a great influence on the morale of their teams as the inclusiveness they promote leads to high motivation, engagement, loyalty, and retention.
Relevance of the theory in the contemporary corporate world
By applying this theory of leadership, modern-day business leaders can foster a strong sense of belonging among their employees which can lead to exceptional performance. To validate, as cited by BetterUp, a strong sense of workplace belonging leads to a 56 percent increase in the productivity of employees. Moreover, it can also lead to a 50 percent reduction in employee turnover and a 75 percent downfall in employee sick rate. Certainly, participative leaders can help organizations overcome the risks of high costs of employee turnover.
Needless to say, when employees’ participation in the decision-making process will be genuinely encouraged, the sense of workplace belonging will be massive. Participative leaders have the best prospects of fostering strong workplace belongingness and cohesion among teams.
Also, participative leaders are looked at by their followers with profound respect and loyalty. This respect further encourages employees to deliver on the expectations of their leaders and go the extra mile to support their leaders. There will be high trust among employees for participative leaders. This is where participative leaders can actually build considerable competitive advantages within their organizations by utilizing the human capital in a highly efficient manner.
A real-world example of a participative leader
Julia Sweet leadership style analysis
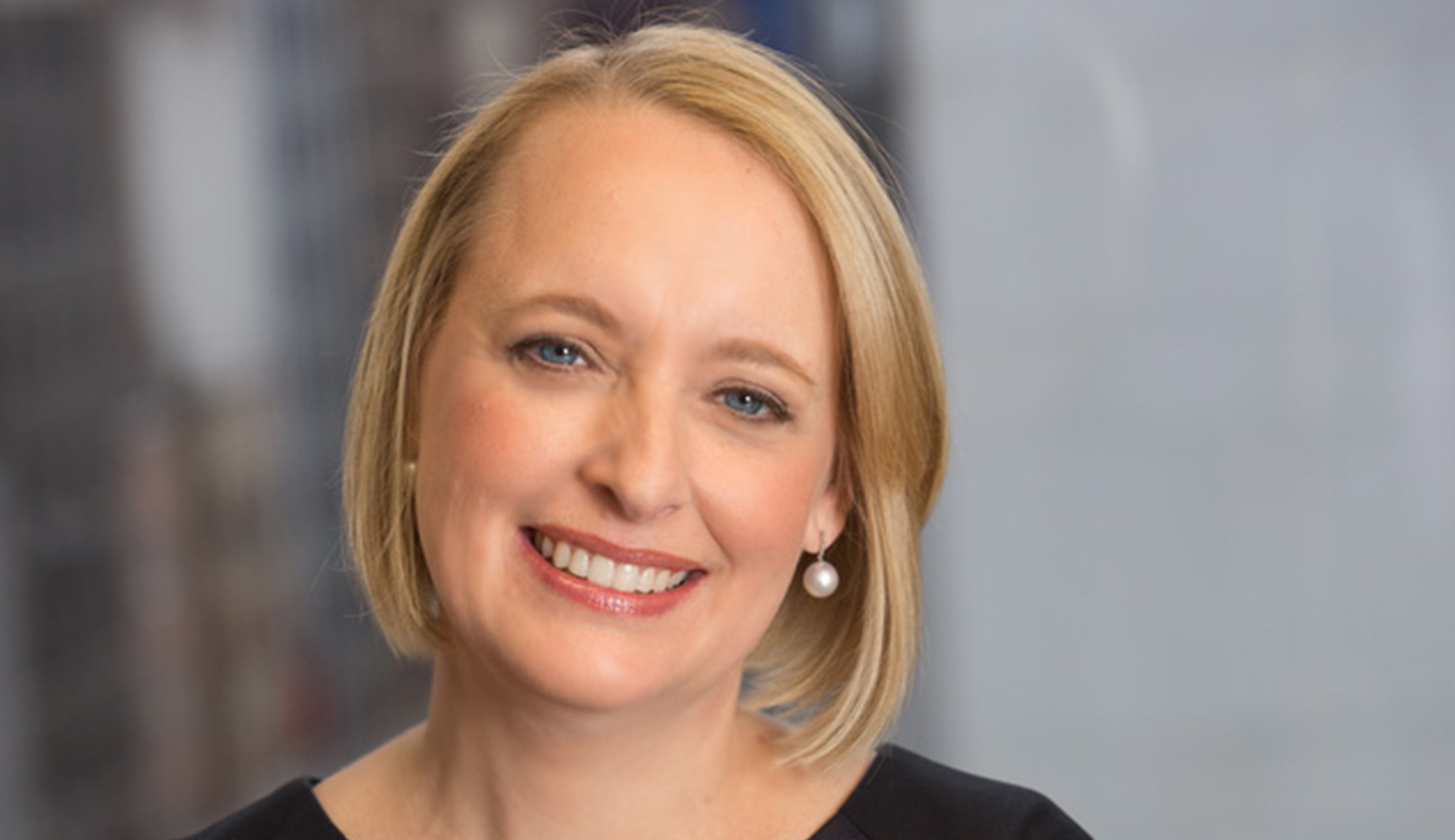

There is no denying the fact that inclusive decision-making can lead to the most brilliant decisions and lead an organization to new verticals of success and advancement. For Accenture, its inclusive decision-making is one of the core competencies that make it a Fortune Global 500 Company.
Accenture is an IT services and consultancy services company headquartered in Ireland and its global presence is a testament to its prolific success. In fact, what has added immensely to the success of the company is the participative leadership of Julia Sweet, the incumbent CEO and Chairperson of the company. Julia Sweet took over the CEO in 2019 and her leadership style is highly popular for promoting a great sense of belonging among employees through inclusion.
Between 2019 and 2021, the annual revenue of Accenture has witnessed an increase from USD 43215 million to USD 50,533 million. In fact, in the second quarter of 2022, the company posted a revenue of USD 15 billion which speaks for the prolific financial position of the company.
The incredible augmentation in the financial position of Accenture has a lot to do with the leadership style of Julia Sweet. She embraces a people-first culture within the company and encourages employees to share their viewpoints and recommendations during the course of crucial decision-making. She is committed to investing in the culture of the company such that employees are comfortable in putting forth their opinions without any reluctance. Besides, with humility, affection, and empathy, she makes employees feel valued and entitled to opinions.
In fact, with collective input and inclusive decision-making, Julia Sweet has initiated a very effective culture of progressive decision-making and change management models within Accenture. To substantiate, in 2020, the company decided to overhaul its growth model for better business results. As a part of the change management plans, the organization collectively decided to arrange its capabilities in leading the market into 4 services including operations, interactive, strategy & consulting, and technology. Furthermore, Accenture also announced its decision to expand its global management committee for better global outreach and has committed to a more proactive digital transformation to meet evolving client needs.
This is one of the many progressive and effective changes that Julia Sweet has brought to Accenture’s approach by putting inclusive decision-making at the epicenter of change management. With her participative leadership, vision, and ability to get the best out of employees by making them feel valued, Julia Sweet is rescripting the success story of Accenture in golden ink. This is what makes her one of the most effective and successful women leaders in the contemporary corporate world.
FAQs
How does participative leadership differ from other leadership styles?
Participative leadership differs from other leadership styles in the level of employee involvement in decision-making. While participative leaders seek input and feedback from their team members, other leadership styles, such as autocratic leadership, rely more on the leader's authority and decision-making without extensive input from the team.
What are the potential challenges of implementing participative leadership?
While participative leadership has numerous benefits, still due to multiple people involved in decision-making, it can be a time-consuming process. Additionally, a lack of expertise among team members to whom you assign responsibilities can hamper the effectiveness of decisions made.
How can a leader transition to a participative leadership style?
A leader can transition to a participative leadership style with the help of the following steps:
Promote Open Communication: Encourage team members to share their ideas, concerns, and feedback openly.
Delegate Decision-Making: Delegate decision-making authority to team members and involve them in setting goals and targets.
Build Trust: Establish trust by demonstrating respect for team members' input and valuing their contributions.
Provide Support: Support team members as they take on more responsibilities and embrace their role in the decision-making process.
Next Theory
Leader Member Exchange Theory of LeadershipNext Theory
Path-Goal Theory of Leadership
 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register