Lyft Overview
Lyft is an eminent American company that offers ride-hailing, vehicle rental, bicycle sharing, food delivery, and other services in the US and Canada. Besides, the company is one of the direct competitors of Uber and has a market capitalization of USD 12.98 billion. This article puts forth an elucidated and extensively researched SWOT Analysis of the company taking into account all the concurrent and relative internal and external factors.
To add, the Lyft SWOT Analysis can be used as an effective planning tool by the company to analyze how its present competitive position compares with its competitors and the same can be improved. In case you wish to learn about conducting a SWOT analysis in detail, you should definitely go through our meticulous Swot Analysis guide. So, let’s get started without further ado.
Table of Contents
An elaborative SWOT Analysis of Lyft
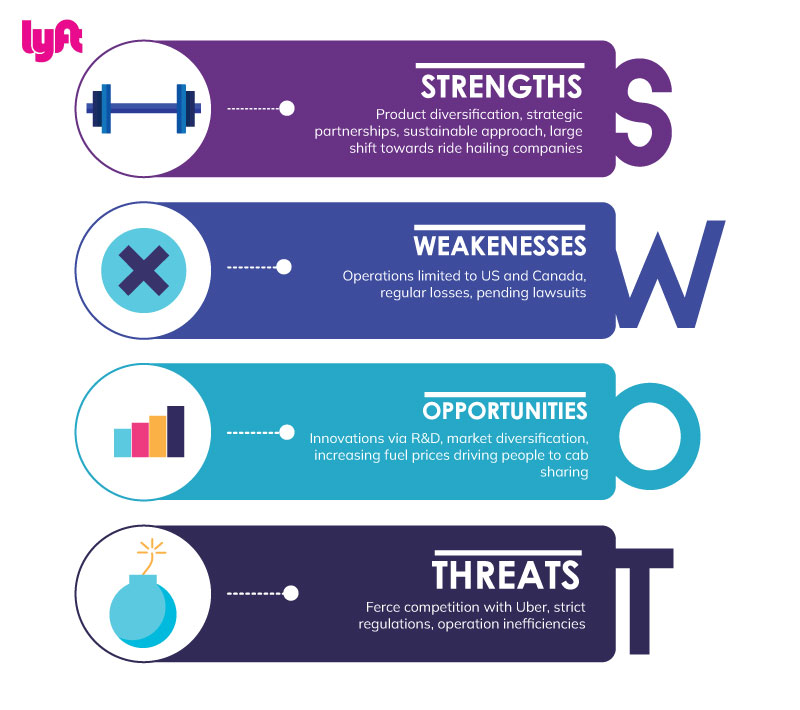
Lyft Strengths
- Diversified products- Lyft has a range of products in its portfolio that include shared taxis, shared scooters, rental bikes, and cars along with a food delivery platform. The diversified portfolio can provide it with an advantage over the competitors.
- Strategic partnerships- Lyft has collaborated with various companies such as Starbucks, Delta, and HERE Technologies among others. The first-time riders can earn points for using Lyft and they can redeem them at Starbucks to get free food (Starbucks, 2016). Further, partnership with Delta enables the customers destined towards the airport to receive traveler reminders and in-ride flight status updates (Lyft, 2021). These partnerships can enhance customer satisfaction, thereby leading to an increase in sales.
- Sustainable initiatives- Lyft is focused on environmental sustainability and for this, it had launched an electric vehicle program in 2019 and has inducted 1000’s hybrid electric vehicles till now. Further, it is a member of We Are Still In which is an initiative by a group of companies to support the Paris Accord. In addition, it plans to convert the whole fleet in its network to the electric mode by 2030 (Lyft, 2020).
- Strong rider growth- The riders have grown significantly over time. In 2020, the ridership per quarter averaged 13.75 million whereas it increased to 17 million per quarter in 2021, thus, highlighting a positive outlook for the company (Wilhelm, 2022).
Lyft Weaknesses
- Consistent losses- Lyft has been incurring continuous losses from the last 5 years and they lost $683 million in 2016, $668 million in 2017, and $911 million in 2018 (Grisworld, 2019). Its loss widened in 2020 to $1.8 billion and in 2021 it lost $1 billion (Lyft, 2022). The consistent losses can lead to more cash burning, thereby leading to a reduction in net cash flows and posing threat to its long-term sustainability.
- Limited to the US and Canada- Lyft is currently operating in the markets of the US and Canada. Such limited presence is not sufficient to sustain in the globalized environment. Lyft should look to expand its presence in the top economies of the world like Brazil, India, and China.
- Involved in various lawsuits- Lyft has been involved in various lawsuits that include over a dozen lawsuits for the sexual assault in its taxis (Paul, 2021). Furthermore, the company has been sued by investors for not disclosing the information relating to assaults before the launch of its IPO. Also, it is engaged in a tussle with the US Department of Justice over the discrimination meted out to disabled people in its taxis (Dickey, 2020).
Lyft Opportunities
- Market diversification- Lyft is just limited to two countries and it can venture into other potential markets like India, Australia, Europe, etc. that would increase its profitability.
- Research and Development- Lyft can increase its budget on research and development which is currently limited to $909 million. The increase in R&D would provide Lyft with an opportunity to discover innovative ways to enhance its competitive position.
- Larger subscription to cab sharing services- Since fuel prices are rising at an enormous pace and the trend is expected to continue because of the disruptions caused by the Ukraine-Russia conflict, more people will be looking to avoid using private cars. This is where there lies a massive opportunity for the global ride-hailing industry and hence, Lyft.
Lyft Threats
- Intense competition- Lyft faces intense competition from Uber that has a market share of 68% in the US ride-sharing market. It also has a high customer loyalty at 63%, thereby posing a great threat to Lyft (Dean, 2021).
- Regulatory threats- The ride-sharing market until recently was not highly regulated but various regulations have emerged now that include rules for classification of gig workers and imposition of sales tax on rides among others. This can result in complexities and an increase in the cost of operations.
- Operational inefficiency due to pandemic- The pandemic has resulted in disruption in the operations and the company is facing a shortage of drivers because of which customers have to wait for longer times. Also, the company has to incur more expenses in order to retain the drivers (Siddiqui, 2021).
Also, you can read the PESTLE Analysis of Lyft to determine how the macroenvironment factors influence the company or the automotive industry.
Recommended Readings
References
Dean, B. (2021). Uber Statistics 2022: How Many People Ride with Uber?. backlinko.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://backlinko.com/uber-users
Dickey, M. (2022). Lyft settles DOJ lawsuit alleging violation of Americans with Disabilities Act. techcrunch.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://techcrunch.com/2020/06/22/lyft-settles-doj-lawsuit-alleging-violation-of-americans-with-disabilities-act/
Griswold, A. (2019). Lyft warns it may never make any money. www.qz.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://www.qz.com/1563655/lyft-ipo-filing-shows-a-history-of-losses-and-no-clear-path-to-profitability/amp/
Lyft. (2020). Environmental, Social, & Corporate Governance Annual Report. s27.q4cdn.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://s27.q4cdn.com/263799617/files/doc_downloads/esg/Lyft_ESG_Report_2020.pdf.
Lyft. (2021). Lyft and Delta Expand Partnership to Provide Smoother Experience for Travelers with In-App Flight Status and Additional Reminders. www.lyft.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://www.lyft.com/blog/posts/lyft-and-delta-expand-partnership-to-provide-smoother-experience.
Lyft. (2022). Lyft Announces Solid Q4’21 and Fiscal 2021 Results. investor.lyft.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://investor.lyft.com/news-and-events/news/news-details/2022/Lyft-Announces-Solid-Q421-and-Fiscal-2021-Results/default.aspx
Paul, K. (2021). Lyft admits it recorded 4,000 sexual assault claims in long-awaited report. theguardian.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://theguardian.com/technology/2021/oct/22/lyft-sexual-assault-reports-uber-ridesharing
Siddiqui, F. (2021). Where have all the Uber drivers gone?. ww.washingtonpost.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2021/05/07/uber-lyft-drivers/.
Starbucks. (2016). Starbucks Rewards Members Can Earn Stars with their Morning Commute. stories.starbucks.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://stories.starbucks.com/stories/2016/starbucks-rewards-members-earn-stars-with-lyft/.
Wilhelm, A. (2022). Lyft’s revenue growth masks active riders slippage. techcrunch.com. Retrieved 14 March 2022, from https://techcrunch.com/2022/02/08/lyfts-revenue-growth-masks-active-riders-slippage/amp/.

 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register