H&M Overview
Hennes & Mauritz AB (STO: HM-B) also known as H&M is one of the most renowned brands all over the globe. This Swedish clothing retailer brand was originally founded in 1947 and today the company holds 4,743 stores in over 50 countries. Although H&M is one of the biggest retail players in the clothing industry, in order to maintain its competitive advantage, the company needs to constantly work on strengthening its internal capabilities. That being the case, in order to optimize its strengths, eliminate its weaknesses, grab the opportunities, and prevent threats, the company needs to conduct an effective SWOT analysis.
To elaborate, SWOT analysis is an effective management tool that can assist companies in determining their internal strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. These identified factors can assist companies in optimizing their core competencies and gaining a competitive edge over their competitors.
That being the case, this blog will effectively highlight the SWOT analysis of one of the most prominent clothing brands in the world, H&M. Additionally, if you want to gain extensive insights on SWOT analysis, you can have a look at our complete and extensive SWOT analysis guide. Till then, let’s get started with an in-depth H&M SWOT analysis.
Table of Contents
Extensive and Detailed SWOT Analysis of H&M
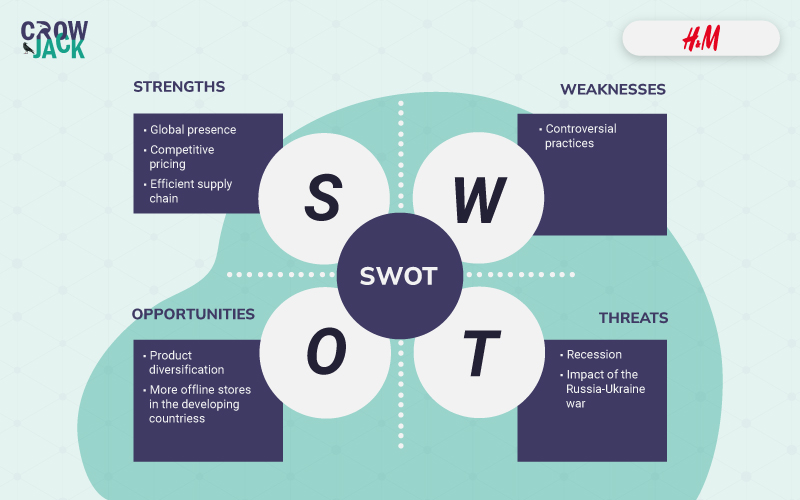
Strengths of H&M
Global presence- H&M group has an extensive presence across the top economies of the world. Its portfolio consists of brands like H&M, COS, Monki, Weekday, & Other Stories, ARKET, Afound, and H&M Home. All these brands have physical stores as well as online markets except the Afound which is just available online. The total store count as per the company’s website is 4702 and has a presence in 76 countries. Further, the company is considered to be the fourth most valuable apparel brand after Nike, ZARA, and Adidas as per the findings of Statista.
Competitive pricing- One of the major advantages of H&M is that its prices are low as compared to the competitors even though it is considered a luxury brand. As per the article on LinkedIn, the company is able to keep the prices low by outsourcing most of the manufacturing to the manufacturers in countries that have cheap labor. For example, the products that are sold in Europe are mostly manufactured in Turkey and the basic product range gets manufactured in Asian countries.
Huge variety of products- H&M deals in various products that include sportswear, underwear, cosmetics, accessories, and shoes while it caters to different segments such as men, women, teenagers, children, and babies.
Strong online presence- H&M has its own online marketplace in around 54 markets. Further, the company has also tied up with different third-party e-retailers such as Myntra in India (Crossley, 2019). Further, it is also experimenting with selling products of other brands such as Crocs, Fila, Lee, and Wrangler on its website in two countries, Sweden and Germany (Anderson, 2022).
Efficient supply chain- H&M’s has a huge supply chain network that consists of over 602 suppliers and 1519 factories along with effective change management capabilities. The network is scattered across different nations from Africa, Asia, Europe, and North America. Further, the company works on the principle of transparency and is a member of the transparency pledge. The details of all the suppliers are disclosed in the public domain including the name of the supplier, the location, and the product type (H&M, 2022).
Further, the company has formulated a supplier’s code of conduct that require the suppliers to purchase the textile from the manufacturers that produce it in a sustainable manner and the suppliers must adhere to ethical standards such as payment of fair wages to the workers, no deployment of forced or child labor. In addition, inventory management has been made much more efficient by the use of artificial intelligence for the forecasting of demand and this has resulted in a decline in waste of the clothing (Britt, 2020).
Effective organizational structure- H&M functions through a matrix organizational structure wherein there are multiple brands and each brand is controlled by a different individual and each one of them has its own respective sales team. This organizational structure is beneficial for the organization as there is efficiency in communication and also each employee is clear about their role and objectives in the organization.
Weaknesses of H&M
Controversial practices- H&M has been in the news many times for all the wrong reasons. In 2018, the company had to face protests because of its racist advertising wherein a black child was wearing a sweatshirt with the slogan that read “coolest monkey in the jungle”.
As a result of such ethical issues, the company’s stock prices declined to a great extent and its stores were vandalized along with many celebrities severing ties with the brand. This ad was the result of the lack of focus of the company on the aspect of diversity and most of its staff in Europe was white (Byrne, 2022).
Further, the company has also been accused of making false claims about the sustainability of its products. One of its products named Antoinette dress was said to have used 20% less water than the baseline, however, the investigation revealed that the usage of water was actually 20% more.
Hence, these practices reflect the urgent need for the company to shift its focus on sustainability which can include more recruitment of employees from diverse backgrounds in the workforce, and training the employees so that they can be more sensitive towards employees with different needs. Also, the company must focus on environmental sustainability and be more transparent and honest toward the customers.
Opportunities for H&M
Product diversification- H&M is already an established brand in apparel and it can exploit the opportunity by venturing into sports apparel which would make it possible for the company to attract more customers. A well-framed business diversification strategy will help the company acquire a larger market share in emerging markets.
More offline stores in the developing countries- Although H&M is already setting up its offline stores in developing countries, it can even come up with more and more offline stores in other developing countries as well to attract new customers and earn high profits contributing to the growth of the company.
Threats for H&M
Recession- As per the analysis by CNBC, a few of the powerful economies in the world are on the brink of recession including the US, UK, and Europe. It is predicted that these economies would go into recession in the coming 12 months owing to the consistent slow growth over the years. The slow growth in these economies would lower the sales of H&M.
Impact of the Russia-Ukraine war- H&M has been at the receiving end because of the war between Russia and Ukraine. As per the Financial Times, the company has now closed 185 stores in Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus. This could have an impact on the company in the long run as before the war, Russia was the sixth largest market for H&M and accounted for 4% of the group sales.
To conclude, H&M has a strong market with customers from all segments and it focuses highly on its supply chain. However, the company has been involved in various controversial practices related to racist products and environmental sustainability which it can improve by training the employees about diversity and employing more people from diverse backgrounds. It also needs to be more honest and transparent towards its valuable customers or else its brand image and value can decline. Besides, H&M PESTLE Analysis gives a more detailed overview of how external business factors affect the company.
Recommended Readings
References
Anderson, G. (2022). H&M opens its e-commerce site to third-party clothing brands. retailwire.com. Retrieved 28 July 2022, from https://retailwire.com/discussion/hm-opens-its-e-commerce-site-to-third-party-clothing-brands/.
Britt, H. (2020). The H&M Supply Chain Could Be the Model to Follow in Making Fast Fashion Sustainable. www.thomasnet.com. Retrieved 28 July 2022, from https://www.thomasnet.com/insights/h-m-supply-chain/.
Crossley, I. (2019). H&M expands online presence by launching on Myntra. in.fashionnetwork.com. Retrieved 28 July 2022, from https://in.fashionnetwork.com/news/H-m-expands-online-presence-by-launching-on-myntra,1129131.html.
Byrne, C. (2022). The H&M Marketing Controversy. stockton.edu. Retrieved 28 July 2022, from https://stockton.edu/diversity-inclusion/h-and-m-marketing-controversy.html.
H&M. (2022). Supply chain. hmgroup.com. Retrieved 28 July 2022, from https://hmgroup.com/sustainability/leading-the-change/transparency/supply-chain/.

 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register