Afterpay Overview
Afterpay is an Australia-based financial service provider that allows customers to pay later for the products that they shop from various merchants both online and in-store. The company is associated with more than 100,000 merchants who offer products in many categories including clothing, accessories, appliances, electronics, entertainment, beauty, cosmetics, etc. (Afterpay, 2021). The company operates in Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, the US, Canada, UK and has a user base of more than 16 million people (Eyers, 2020). The customers are not charged any interest if the payment is made within the time and makes money by charging commission from the merchants that range between 3% to 6% and late fee penalty from customers. Further, it earns around $500 million of revenue a year and is worth $39 billion (Rose, 2021).
PESTLE Analysis is a great tool for evaluating the external environment of an industry or a company. The PESTLE analysis assists the companies in deriving effective mechanisms to deal with the situations in the external environment. This PESTLE analysis would involve the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal factors that can impact Afterpay.
Table of Contents
A Precise PESTLE Analysis of Afterpay
Political factors affecting Afterpay
The Reserve Bank of Australia is planning to bring in a law that would allow merchants associated with Buy Now Pay Later companies to pass on the fees ( commission, surcharge) that they incur to the customers which are now prohibited by the Buy Now Pay Later companies.
This would increase the cost of shopping for the customers and hence they would be discouraged to avail this facility which would lead to a loss of customers for the companies dealing in Buy Now Pay Later services (Duran, 2021). The Buy Now Pay Later payment services are most beneficial to customers that cannot pay at once or even on time and many companies do not even check their credit scores but the new Buy Now Pay Later code established by the Australian Government now makes it mandatory to conduct a financial check before offering the late pay service and has capped the number of late payments that a person can accrue. The new rules would make it difficult for many customers to avail the service, thus leading to a loss of customers for the Buy Now Pay Later companies (Cockburn, 2021).
Economic factors affecting Afterpay
Australia’s economy grew at a rate of 4.7% in 2021 as compared to 2.4% in 2020. Further, according to the analysis done by OECD, the growth in 2022 and 2023 is expected to be 4.2% and 2.6% respectively. The high fluctuation in the economy would result in deviation in the income level of the people as well which would ultimately result in an increase in the credit business of companies engaged in the Buy Now Pay Later segment.
In addition, the unemployment rate is expected to be stable at 4.5% in 2022 and 4.6% in 2023 which means that more and more people would opt for the interest credit facilities which can lead to an increase in the business for the Buy Now Pay Later companies.
The buy Now Pay Later market in Australia is currently valued at $7.35 billion which is expected to increase at a CAGR of 24% till 2028 and reach $52 billion. A high positive outlook for the industry indicates many opportunities for the Buy Now Pay Later companies in Australia to expand their market share (GlobeNewsWire, 2021.
However, some projections also hint that the revenue growth in the Australian buy now pay later services may have to witness a decline in the coming years. The same is represented in the illustration below.
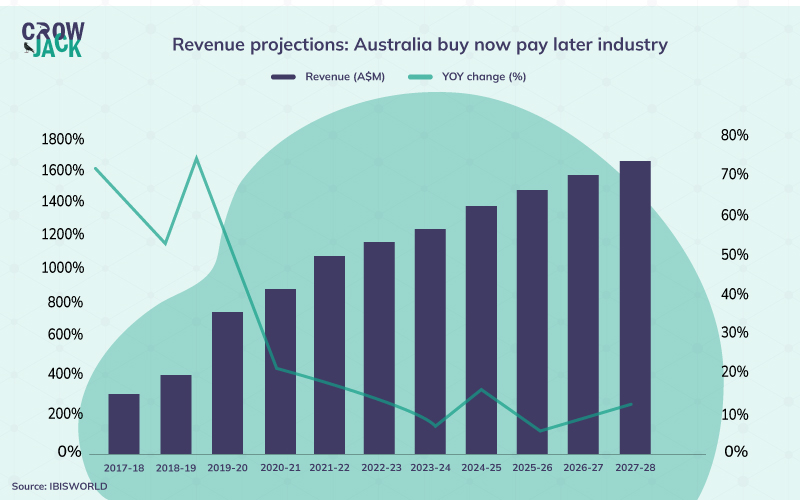
Social factors affecting Afterpay
The cultural dimensions of Australia hint that people in Australia like to get indulged in the gratification of their happiness and embrace a modern lifestyle. Having said that, there is a large market in the country for buy now and pay later services. People in Australia are facing financial constraints as a result of the loss of jobs and businesses due to COVID and thus more and more people are preferring Buy Now Pay Later option for making purchases. This has led to a 55% increase in the transactions made through Buy Now Pay Later services (Williams, 2021).
Technological factors affecting Afterpay
Various technologies have emerged in the Fintech sector including blockchain technology for recording and sharing data across different platforms at once. Further, process automation such as the use of chatbots for interacting with customers and conducting other back-end office operations like a recording of data, and period-end accounting enhances efficiency and leads to a reduction in human errors (Fong, Han, 2021).
Legal factors affecting Afterpay
The new regulations introduced by the Australian Government that make it mandatory for the Buy Now Pay Later companies to conduct a throughout credit check means that the companies can lose out on customers as 80% of the customers that avail of these services do not have a good credit score. This decision would make it difficult for them to avail loans in the future (Australian Banking Association, 2021). Hence, companies will have to work out some effective change management strategies do deal with the rising challenges.
Environmental factors affecting Afterpay
The Australian government has recently introduced amendments in the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act that are aligned to the conventions signed in Paris agreement aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
The companies are now bound to report the annual emissions that are generated from their operations which can impact the Fintech companies in a large way as they are the major producers of greenhouse gas emissions (Australian Government, 2021).
From the above analysis, it can be concluded that after COVID, the instability in the income of the people has risen because of which the Buy Now Pay Later companies to stand a good chance of exploiting the market.
However, the government is becoming stricter regarding the credit check to be conducted by the companies before providing the service to the customers which may limit the scalability of the businesses because they would lose out on their target mark. Besides, to assess the internal strengths and weaknesses of the company, you can go through our meticulously conducted SWOT Analysis of Afterpay.
Recommended Readings
References
Cockburn, G. (2021). New rules for ‘buy now, pay later’ companies in Australia. Retrieved 9 June 2022, from https://www.news.com.au/finance/business/banking/new-rules-for-buy-now-pay-later-companies-in-australia/news-story/8191ac04ab13629774539a8e960acbb8
Duran, P. (2021). Australia's central bank tells 'buy now, pay later' firms to drop surcharge ban. Retrieved 9 June 2022, from https://www.reuters.com/business/finance/australias-central-bank-tells-buy-now-pay-later-firms-drop-surcharge-ban-2021-10-22/
Eyers, J. (2020). Afterpay global users surpass 11 million. Retrieved 9 June 2022, from https://www.afr.com/companies/financial-services/afterpay-global-users-surpass-11-million-20201028-p56983
Fong, D., Han, F., Liu, L., & Qu, J. (2021). Seven technologies shaping the future of fintech. Retrieved 9 June 2022, from https://www.mckinsey.com/cn/our-insights/our-insights/seven-technologies-shaping-the-future-of-fintech
ROSE, T. (2021). How Does Afterpay Make Money (Business and Revenue Model). Retrieved 9 June 2022, from https://entrepreneur-360.com/how-does-afterpay-make-money-13180
Williams, T. (2021). Financial uncertainty amid the pandemic fuels a rise in buy now, pay later services in Australia. Retrieved 9 June 2022, from https://www.nielsen.com/us/en/insights/article/2021/financial-uncertainty-amid-the-pandemic-fuels-a-rise-in-buy-now-pay-later-services-in-australia/

 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register



