Samsung Overview
Samsung is a South Korean company dealing in the manufacturing and selling of electronic products. Various products that Samsung manufactures include mobile phones, TVs, and other audio-visual devices, semiconductor chips home appliances, and products for industrial IT solutions (Samsung, 2022). The company produces around 120 million smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices and its biggest factory is located in Noida, India (Adnan, 2022). The company earned a revenue of $232 billion in 2021, an increase of 18% on yearly basis (GSM Arena, 2022). Samsung is the global leader in the smartphone segment with a 32% market share, ahead of Apple by 4% (Moshfegh, 2020).
However, to sustain its leading position in the industry, Samsung will need to conduct effective strategic analysis at regular intervals to stay aligned with the ever-changing key internal and external factors in the industry. With respect to the evaluation of external factors, the PESTLE Analysis Model will prove to be enormously effective as it looks into different dimensions of the external business environment.
Henceforth, this article presents a diligent PESTLE analysis of Samsung to identify the key external determinants with respect to the smartphones and consumer electronics industry. So, let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Precise and Comprehensive PESTLE Analysis of Samsung
Political factors affecting Samsung
The political environment in South Korea is stable and it has strong fiscal, monetary, and regulatory institutions. Further, the government of South Korea has announced plans to offer financial support worth $451 billion to the companies that are engaged in the production of semiconductor chips in the country. This can be positive news for the electronics industry as they would be able to lower their manufacturing cost because of the subsidies (Moss, 2021).
Moreover, South Korea has a Double Tax Avoidance Agreement with more than 80 countries and this can prove to be beneficial for the companies as they would not have to pay double taxes on the income earned in Korea as well as the source country. However, the shortage of chips due to the Russia-Ukraine war as Ukraine is the main supplier for the neon suppliers required in the semiconductor chips could have an impact on the production in the electronics industry.
Besides, electronic companies can face more financial liabilities as 136 countries led by OECD have introduced plans to impose a 15 percent global minimum tax on companies with revenues above $867.5 million.
Also, the companies with revenues above 20 billion Euros and a profit rate above 10 percent, will have to pay 25 percent of what they make over the 10 percent as taxes in the countries they made the money from (Wook, 2021). The government of South Korea to has imposed sanctions on Russia due to which the electronic companies would not be able to ship their products and this can have a huge impact on their profitability as they would be losing out on a $6 billion electronics market of Russia. Likewise, the US government is also highly stable and has recently approved a fund of $52 billion to subsidize chip manufacturing to tackle the global shortage of chips (Whalen, 2021). The US has a free trade agreement with South Korea under which imports for color video monitors, boards and panels, and many other items for electric products are free of tariffs.
Speaking of emerging markets for the electronics industry, the government of India is promoting electronics manufacturing on a large scale wherein it provides incentives of 4-6% to the companies on their net incremental sales under the Production Linked Scheme (MoEIT, 2022).
The current government of India is discouraging imports from China, the country from where most of the electronic components are imported. For electronics companies based out of China, this could be a great opportunity. China is offering a 30% subsidy to the companies for manufacturing semiconductor chips and has plans to offer $300 billion worth of subsidies by 2025.
Economic factors affecting Samsung
The growth rate of South Korea for the year ending 2021 was 4%, the highest in 11 years (Jaewon, 2022). It is further predicted to decline to 3% in 2022 and 2023 respectively because of the slowdown due to COVID (OECD, 2022). Similarly, the growth rate of the US is predicted to decline to 4% in 2022 and 2.6% in 2023 respectively (Shalal & Lawder, 2022). Further, the inflation in South Korea in 2021 was at a 10 year high of 2.5% and is currently at 3% (Kim, 2022).
Even after reaching an all-time high, the inflation rate is still very much within control so this would not have a huge impact on the sales of the electronics industry (Bartash, 2022). But, in the US, inflation is at a 40 year high of 7.5% because of a reduction in the supply of many goods and services compared to their demand, and the higher inflation rate would reduce the affordability of the products for many people, thus leading to a reduction in the sales for the electronics industry (Bartash, 2022).
In addition, the per capita income of South Korea in 2021 was $35000, the highest since 2010 (Kim, 2021). But, it is expected to drop to the level of $29000 by the end of 2022. And the per capita income of the US was $63, 416 while it is expected to lower to $55000 in 2022 and $57000 in 2023. The high reduction in per capita income can lower the purchasing power of the consumers, thereby leading to a reduction in sales for the companies dealing in electronics products.
Further, China's growth rate at the end of 2021 was 8.1% (Patranobis, 2022). The Chinese economy is expected to slow to 5.1% in 2022 and 2023 (OECD, 2022). The inflation in China was 0.9% in 2021 and is expected to rise a bit to 2.2%. The low inflation rate would mean fewer prices for the products in the market which would ultimately lead to an increase in sales for the products.
India, one of the major markets for the electronics industry is expected to grow at 8.3% by the end of FY2021 (FY, 2022). Further, the economy is expected to grow at 8.7% in 2022 and 6.6% in 2023 (Singh, 2022). Such a high growth rate can be a positive sign for the companies in terms of business opportunities.
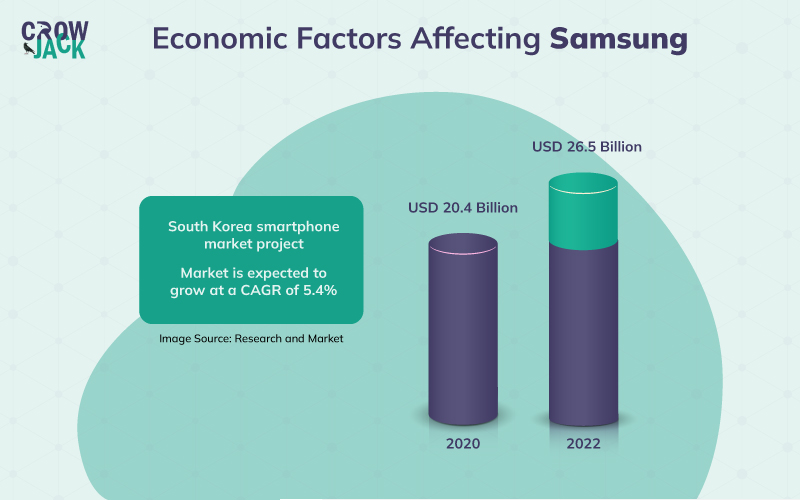
The unemployment rate in India is 6.5%, the lowest since March last year. The rise in employment levels would lead to more stability in the fixed income of the people which would lead to more purchases. The electronics industry in South Korea is the 3rd largest industry and generated sales of over $121 billion in 2020, registering a significant growth over the last year. The industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of 7.6% over 10 years from 2021-to to 2030 (Golden Market Intelligence, 2020). The projected growth of the smartphone industry in South Korea is represented by the following graphic.
Social factors affecting Samsung
The corporate working culture is undergoing a paradigm shift toward remote jobs. Around 75% of South Korean companies are expected to continue working from the home scheme (Business Standard, 2021). Over 22% of the American workforce is expected to work from home by the end of 2022 and it is expected to rise to 26% by 2023 which is expected to rise to 73% by the end of 2028 (Steward, 2022).
The increase in the trend of working from home would lead to an increase in the demand for digital products both for work and leisure. Further, the literacy level in South Korea is 97.9%, and 78% in the US. The high literacy rate means more awareness about operating digital devices, thereby signifying an increase in the interest and sales of digital products.
The positive aspect for the electronics companies in India is that per capita spending on wearable tech has risen by 9%. Talking about China, there is an increase in consumerism and it is expected that over 60% of the products manufactured would be consumed domestically by 2030 as compared to 35% just now. (Zipser &Seong, 2021). In addition, there has been a 39% increase in smartphone usage among people in the last 2 years and the average daily duration has reached 7 hours from 4.5 hours.
The increase in the usage of smartphones presents significant opportunities for electronic companies (Dhapola, 2021). Moreover, global spending on wearable tech is predicted to increase by more than 18% annually over the next 5 years, thus highlighting new opportunities for the companies.
Technological factors affecting Samsung
The R&D budget by the South Korean government for 2022 is pegged at $20.7 billion. Even, the US government is promoting research and development on a huge scale wherein it spent $157 billion on R&D in 2021 and the proposed investment for 2022 is pegged to be $171 billion (Connolly, 2021). India spent Rs. 851 crore in 2021 and the budget has been decreased to Rs. 812 crore for 2022 while China spent 2.78 trillion yuan in 2021 on R&D.
Various new technologies have emerged in the electronics industry including producing electronics with green materials such as microbial components or producing devices with biodegradable and recyclable materials. Further, the use of artificial intelligence in the electronics industry for manufacturing has resulted in improvement in design processes.
It is also being used heavily in predictive maintenance and helps reduce downtime. The Internet of Things is also gaining importance and it enables electronic manufacturing machines to self-process and store data while being digitally connected and it assists in the continuous improvement of the sensors in electronic devices.
Legal factors affecting Samsung
Businesses in South Korea are governed by various laws that include Workplace Safety Act wherein the senior executives of the company can be held liable for work-related injuries and are liable for a fine and one-year imprisonment (Davies, 2021). Further, The Monopoly and Fair Trade Regulation Act prohibits companies from sharing confidential information related to the pricing of products and output and the companies must report the transaction amount and provide details of every merger that exceeds the threshold of KRW 30 billion.
In addition, the US government has also formulated strict antitrust laws that restrict companies from engaging in mergers to reduce competition in the market. Further, it is illegal under The Sherman Act to fix prices, divide markets, or rig bids (Federal Trade Commission, 2022). Furthermore, the increase in the minimum wage in 24 states would lead to an increase in the cost of operations for the companies as they would have to incur more on wages and salaries of the employees (Soergel & Clarke, 2021).
Alongside, the Chinese government has amended its e-commerce policy wherein the companies are now prohibited to impose any restrictions, conditions, or fees on merchants and if the companies want to conduct online business, they would have to apply for a separate business license which was not the case earlier.
The government of India has amended the labor code. The new code on industrial relations provides the companies freedom to lay off employees or close the business without the government's permission, hence easing the prospects of doing the business (Vanamali, 2021).
Environmental factors affecting Samsung
The electronics industry contributes about 3% to the greenhouse gas emissions in South Korea. Further, the electronics industry generates about 0.8 million tonnes of e-waste each year and the government of South Korea has initiated various steps to control the pollution generated out of waste. This includes a GHG emissions trading scheme under which the emissions rights are allocated to companies whose total annual emissions are not less than 125,000 tCO2 (Seol & Kim, 2021). The electronics industry can highly benefit from this scheme as it would help it lower the emission count legally.
Further, the US is a signatory to the International Paris Agreement and as a result aims to cut down carbon emissions by 50% by 2030 (White House, 2021). Furthermore, the electronics industry produces lots of electronic waste in the form of mercury, lead, arsenic, cadmium, selenium, chromium, and flame retardants.
The e-waste regulations in 25 states of the US require companies to mandatorily recycle and reuse the waste generated. Also, the government of China has formulated an action plan under which 50% of the e-waste generated by the companies would have to be recycled. Hence, the requirement for recycling would lead to an increase in expenditure for the companies for establishing the infrastructure. To cope up with the increasing strictness in environmental norms, companies will need a strategic approach to change management to implement the prerequiste transformations.
To encapsulate, the electronic companies can benefit from the fact that South Korea is incentivizing the manufacturing of semiconductor chips which is an important element for electronic products. The growth rate for both the US and South Korea is moderate but the inflation for the US is at an extreme level. This can be a negative aspect for the companies as the prices of the products would rise which can impact the sales of the products.
The increase in the work from home trend and increase in consumption of mobile phones can increase the sales for the companies. The US and Korea have strict laws regarding the formation of cartels and indulging in monopolies so the companies should be aware of that. Besides, the opportunities and threats for Samsung can also be viewed in terms of the companies strengths and weaknesses. For that, you can read our meticulously researched SWOT Analysis of Samsung.
Recommended Readings
References
JAEWON, K. (2022). South Korea GDP growth hit an 11-year high in 2021 on strong exports. /asia.nikkei.com. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://asia.nikkei.com/Economy/South-Korea-GDP-growth-hit-11-year-high-in-2021-on-strong-exports
JEONG, L. (2021). Government sets a ₩23.5 trillion budget for R&D in 2022. koreajoongangdaily.joins.com. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://koreajoongangdaily.joins.com/2021/06/24/business/economy/RD-Science-and-Technology/20210624183600347.html#:~:text=The%20Presidential%20Advisory%20Council%20on,increase%20compared%20to%20this%20year
Kim, C. (2021). S.Korea Dec inflation at 3.7%, 2021 rate at a decade high of 2.5%. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://www.reuters.com/markets/asia/skorea-dec-inflation-37-2021-rate-decade-high-25-2021-12-30/
Kim, I. (2021). Korea 2021 GNI per capita to top $35,000 to record high. /www.kedglobal.com. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://www.kedglobal.com/[exclusive]_economy/newsView/ked202112060001
LEE & KO. (2020). BILL TO AMEND THE MONOPOLY REGULATION AND FAIR TRADE ACT PASSED BY THE NATIONAL ASSEMBLY. www.legal500.com. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://www.legal500.com/developments/thought-leadership/bill-to-amend-the-monopoly-regulation-and-fair-trade-act-passed-by-the-national-assembly/.
Moss, S. (2021). South Korea is to spend $451 billion on becoming a semiconductor manufacturing giant. www.datacenterdynamics.co. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://www.datacenterdynamics.com/en/news/south-korea-to-spend-451-billion-to-become-semiconductor-manufacturing-giant/.
Mukherjee, W. (2022). Indians are again spending on electronic goods Read more at: https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/cons-products/electronics/indians-are-again-spending-on-electronic-goods/articleshow/89555062.cms?utm_source=contentofinterest&utm_medium=text&utm_campaign=cppst. /economictimes.indiatimes.com. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/cons-products/electronics/indians-are-again-spending-on-electronic-goods/articleshow/89555062.cms?from=mdr.
OECD. (2021). Economic Forecast Summary (December 2021). www.oecd.org. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://www.oecd.org/economy/korea-economic-snapshot/#:~:text=The%20Korean%20economy%20continues%20to,%2C%20averaging%20close%20to%203%25
PwC. (2022). Tax information exchange agreements (TIEAs). taxsummaries.pwc.com. Retrieved 4 April 2022, https://taxsummaries.pwc.com/republic-of-korea/individual/foreign-tax-relief-and-tax-treaties#:~:text=Korea%20currently%20has%20social%20security,%2C%20Quebec%2C%20Romania%2C%20Slovakia%2C
Zipser, D., & Seong,, J. (2020). Five consumer trends shaping the next decade of growth in China. /www.mckinsey.com. Retrieved 4 April 2022, from https://www.mckinsey.com/cn/our-insights/our-insights/five-consumer-trends-shaping-the-next-decade-of-growth-in-china.

 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register



