
Overview
In the contemporary world, organizations lay great emphasis on the business environment. In fact, the business environment is a key determinant of strategic planning, change management, and goal setting that companies undertake to stay ahead in an enormously competitive business ecosystem. Having said that, the environmental analysis holds great significance in terms of business planning. The business environment and marketing environment are both essential for businesses to thrive and advance towards greater scalability.
Table of Contents
Further, it is important for you to know that both the business environment and marketing environment are broadly categorized into two classifications. To explain, micro and macro environment are the two major bifurcations of business environment and marketing environment.
In this blog, we shed light on what the macro environment is with respect to business planning and marketing. The blog elaborates on the macro environment definition, macro environment factors, and its applicability for businesses. So, let us get started without further ado.
What is Macro Environment
A macro environment can be understood as the mix of external factors that affect decision-making, strategic planning, and operational strategies at organizational levels. To discuss further, the macro environment with respect to a country or specific geographical area including political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors that can have a direct or indirect influence on industries. In simpler terms, the macro environment takes into account the broader picture with respect to the state of the external environment.
Here, it is imperative to note that a macro environment is always external to the organization and looks at the set of overall external factors that affect the entire industry. For instance, when the top management at Apple will be conducting a macro environment analysis, it will look into external factors with respect to a country or location that affects the entire consumer electronics industry.
Macro environment in business
To further explain, when organizations undertake strategic planning in terms of expansion to new markets or other business objectives, the external environment has a massive role to play. Let’s say a company has to expand into a new market in one of the emerging markets. For the company to be able to formulate an effective expansion strategy, the overall political, economic, and social environments and their influence on that industry will be a major consideration. Similarly, the legal framework in the country and the environmental norms that affect the industry in the country will also be a major consideration.
While the micro environment in business delves into factors like competitors, the influence of customers or suppliers, trade unions, market intermediaries, and so on, the macro environment looks at the overall environment prevailing in the industry with respect to a specific market or country. This is where the major difference between micro and macro environment lies. Also, when it comes to the macro environment, companies or governments cannot really completely control the macro environment.
Further, in the context of macro environment analysis, businesses apply various strategic planning models to assess macro environment factors. For instance, PESTLE analysis is a widely applied strategic planning model that organizations implement to examine the business environment external to the company. What are the macro environment factors that we are talking about? How do these factors influence business decisions and strategic planning at organizational levels? Let’s find out in the subsequent section.
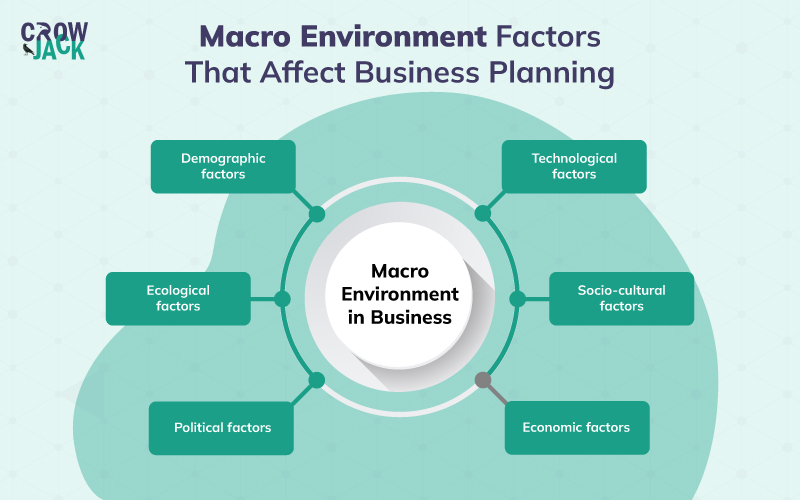
Macro environment factors you need to know
The macro environment factors in business influencing strategic planning and change management at the organizational level are broadly categorized into the following segments.
1. Demographic factors
An analysis of demographics takes into account the divisions of populations in terms of age, gender, race, income, profession, and other factors with respect to population. An analysis of demographic factors has a vital role to play in strategic planning.
When it comes to product diversification or entering a new market, the population demographics with respect to that market will be significant in decision making. To explain, when it comes to segmentation of the target audience for a product or service, the demographic division will be an essential dimension of segmentation.
In the ultimate sense, for business success, organizations need to identify the demographic breakdown of their niche target audience and deliver on their expectations for worthwhile customer experiences.
Let us try to understand the significance of demographic factors through an example. Let’s say a premium smartphone brand plans to expand to a developing nation like. Now being a premium smartphone brand, the company will only want to cater to the premium segment customers. This is where the demographic context of income levels will have a huge role to play. The target audience of this brand will be the upper financial segments that can spend on premium phones. If there are not many people in the country that have above-average income levels, the idea of expansion may not seem beneficial.
Similarly, for most businesses, millennials and Gen Z folks make the most important markets. So, a country where millennials and Gen Z make up the most considerable part of the population will be an ideal market for brands. Makes great sense, right?
This is how demographic factors prove substantial for businesses. This explains why businesses pay great heed to the demographic segments of their niche market.
2. Ecological factors
Ecological factors correspond to the natural factors pertaining to a country or a geographical region. In simpler terms, ecological factors define the convenience of access to key natural resources that are vital for supply chain operations and production.
If companies have easy access to natural resources that are required in a recurring manner for key operations like production, assembly, or distribution, it will certainly add greater value to business success. On the contrary, if a geographical area is such that the supply of natural resources is scarce, not only will it add to the operational cost but also increase the risk of unprecedented delays in operations.
For instance, the food and beverages industries are a lot dependent on water resources. As per the Water Footprint Network, beverage companies use more than 600 liters of water in the production of a 2-liter bottle of soda. Hence, it is important for beverage companies to set up their plants and production units in areas that have an abundance of water resources.
3. Political factors
Political factors play a very crucial role in strategic planning at the organizational level. The political scenario of a country is a major determinant for companies to continue their operations, expand to the country, or make future strategies for business growth in the country.
As a business owner, would you like to expand to a country that has an unstable government or harsh taxation policies? For your company’s expansion, you would rather want to enter a market where the political environment is stable and there are attractive tax rebates for industries.
With respect to the political environment of a country, the following considerations are vital.
Does the government offer subsidies?
Are the taxation policies favorable or not?
What is the state of FDI norms in the country?
What are social welfare policies or CSR policies?
Is the legal framework a hindrance for industries?
To cite an example, most international brands are now entering the Indian market given the favorable and thriving political environment in the country. In some sectors, the Indian government even allows a hundred percent FDI making the country highly attractive to companies. Besides, the country has strong diplomatic relations with the strongest economies of the world and has signed various free trade agreements. All these factors make India one of the most sought-after countries for global trade and commerce.
4. Economic factors
Cost, profits and net present value are the most important considerable metrics for each and every type of business. If you are a business owner, you will ultimately measure the success of your business in terms of numbers that correlate to profitability, sales, revenue, and so on. Hence, in terms of macro environment analysis, taking economic factors into account is highly vital.
Economic factors with respect to a market include determinants like inflation rate, GDP growth projections, exchange rates, industry growth rate, price index, and interest rate. Also, the per capita GDP income in the country and the unemployment rate are key factors to analyze.
To explain the context, if there is economic stability in a country and growth projections are promising for industries, enterprises will get the confidence to invest. On the contrary, if an economy is not doing well as in the case of Sri Lanka, companies will rather want to withdraw.
Hence, the economic prosperity of a country and the key economic trends form an important part of the business macro environment. If the macro environment with respect to industry growth projections and GDP projections is favorable, companies will embrace the idea of expansion without a second thought.
5. Socio-cultural factors
Another important dimension of the business macro environment is the set of socio-cultural factors that define the cultural and social trends in a market. These social and cultural trends have a direct correlation with consumer preferences and shopping patterns in a country. Needless to say, to stay ahead of the competition, it is vital for contemporary businesses to formulate strategies that have consumer preferences at the epicenter.
Probing further, customer needs and wants are often influenced by their cultural norms and social habits. For instance, beef consumption is banned in India given the religious and cultural significance of cows in the country. On the contrary, beef consumption is one of the most common needs of American consumers because their culture does not hold them back from consuming beef. So, when an American meat brand looks to enter the Indian market, it will have to alter its product portfolio for the Indian market.
Moreover, social factor examples can also include e-commerce trends in a country. In some countries, there is a greater preference for online shopping while in others, people have a greater preference for shopping offline. Subject to this trend, businesses need to keep flexibility in their distribution channels.
All in all, for greater success, companies need to keep up with the latest social and cultural trends that have a direct impact on consumers’ buying preferences and patterns. Given the dynamic nature of social trends, companies need to plan for effective change management. An understanding of Hofstede’s cultural dimensions can be of great help for organizations.
6. Technological factors
Last on the list of macro environment factors is the assessment of a country’s level of technological advancement. As we know, every industry today is going through a technological revolution, and the overall business environment is embracing disruptive technologies.
Companies are more interested in exploring markets wherein there is impressive technological advancement and emerging technologies have attained maturity. Basically, the technological infrastructure should be supportive of processes like business automation, remote working, advanced testing, performance testing, digital communication, and so on.
If we talk about countries like the US, China, Japan, Germany, or Russia, these countries have acquired next-level technological capabilities and their technological infrastructures can offer crucial competitive advantages to any industry. On the other hand, countries like Bangladesh, and Indonesia are yet in the process of developing technological capabilities that can give a major boost to industries Global innovation rankings have a huge impact on companies’ approaches to strategic planning.
Nations with exemplary innovation capabilities make the ideal choices for multinational companies looking for business expansion.
Now that we have understood the macro environment in business with attention to detail, the next section explains the concept of the macro environment in marketing.
Macro environment in marketing

The macro environment in marketing is inclusive of the external factors or influences that have a direct or indirect impact on the marketing strategies of a business. It is a well-known fact that marketing is among the functional areas of business operation. Effective marketing could well be the underlying difference between a highly successful business and a business struggling to get desired results in terms of market penetration.
In the contemporary world, marketing has new dynamics altogether. With most businesses going online, marketing has become quite synonymous with digital marketing through social media and search engine marketing. Statistically speaking, the global market size for digital marketing in 2021 was USD 56.5 billion as per Grand View Research. By 2030, this market is projected to grow at an impressive compound annual growth rate of 19 percent.
Moreover, interestingly, as per Statista, the global spending on digital marketing is more than 600 US dollars in 2022. Clearly, businesses are spending on digital marketing with all their heart. However, the formulation of marketing strategies and the success of marketing approaches is largely dependent on the macro environment.
Further, speaking of the factors linked to the macro environment in marketing, the macro environment factors that affect marketing strategies or the marketing mix of a company are explained below along with their impact.
1. Demographic factors
Demographic segments and divisions in a country can have a huge impact on an organization’s marketing strategies. Subject to variations in different population groups and their preferences, companies need to show greater flexibility in their marketing tactics and pricing strategies.
For instance, if in a country, the millennial and Gen Z population is much higher than baby boomers and Gen X shoppers, companies can run sponsored ads on social media as millennials and Gen Z are quite active on social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, Snapchat and so on. In fact, a large proportion of millennials search for new businesses and brands online.
2. Political factors
As in the case of business planning, the political environment of a country also has a great influence on the marketing strategies of a company. Companies have to frame their marketing and pricing strategies as per the prevailing political environment.
For instance, if there are anti-monopoly laws in place, companies cannot exploit pricing strategies by creating monopolies. Also, we can understand the influence of political factors on marketing strategies through another example. In Norway, there is a complete ban on advertising alcohol brands on TV or even on billboards. Hence, the liquor brands in the country have to be considerate of this ban and have to find ways for indirect brand promotions.
3. Economic factors
We saw above how economic determinants and metrics hold immense significance in the analysis of the macro environment in business. Similarly, the assessment of economic factors is also crucial for strategic planning with respect to marketing mix and marketing strategies.
To explain, if the per capita income in a country is high, businesses can go for a premium pricing strategy for their products or services. However, if the personal disposable income levels are low in a country, a premium pricing strategy will not be the best-fit pricing strategy for that market.
Since pricing is an imperative element of the marketing mix, the economic determinants of a country have a direct correlation with pricing strategies. Also, if the industry growth rate is high in a country, companies will not mind allocating additional funds to marketing channels given the scope of a high return on investment.
To cite an example, in the United States, Apple products have a normal perception among consumers given high-income levels in the country and the affordability associated with it. On the contrary, in emerging markets like India or Bangladesh with lower personal incomes , the perception of Apple products is that of premium segment products. So, the company can use this income disparity in emerging markets to market its products in association with a sense of financial superiority to consumers. On the other hand, the marketing approach will be different in the US.
4. Technological factors
In contemporary times, marketing has immense dependence on technological innovations. To explain, emerging technologies like AMP, 5G, blockchain, AI and other innovations are changing the marketing landscape for the better. For instance, the market size of AI in marketing is expected to reach 40.09 billion by 2025. This clearly speaks on behalf of a technological revolution transpring in marketing. With digital tools and automation software, companies have been highly successful in expanding their outreach in a targeted way.
Hence, from the marketing perspective, the technological environment in a country is a significant consideration for companies. The companies will have to determine the best-fit marketing strategies in alignment with the technologies supported by the country. For instance, if a country has a 5G infrastructure or not will be a key determinant for mobile marketing or online marketing. While China and the US already have an extensive 5G presence, developing nations are yet to launch 5G connectivity.
5. Cultural factors
Cultural factors include social trends, religious virtues, ethics, consumption patterns, and other factors that collectively form the culture of a place. With respect to marketing strategies, violating the cultural sentiments of a country or a significant religious group in the country can prove to be detrimental to a company. Having said that, in their promotional strategies, it is important that companies are considerate of the emotions and sentiments that are intrinsic to the prevailing culture.
For a better understanding, let us understand the configuration of the 4 Ps of the marketing mix. The 4Ps of the marketing mix include product, place, price, and promotion. Hence, from the marketing point of view, the product is a highly critical factor. Now, all of us know that pork products are against the cultural views of Islam. So, if a company introduces and markets pork products in an Islamic nation, it can prove to be a disastrous move.
6. Ecological factors
We have already discussed the ecological factors above. Not only are they important for the analysis of the macro environment in business but also in marketing. If natural resources are easily available to a firm in a geographical area, the operational costs will be low and the company can go for a moderate pricing strategy.
However, if the natural resources in an area are insufficient, the operational costs will be high and the companies will need to go for a premium pricing strategy to attain profits. Hence, ecological factors pertaining to a country or area can influence the marketing strategies in multiple ways. This makes the analysis of the macro environment in marketing with respect to ecological or natural factors indispensable.
Recommended Readings
An Explicit Description of Change Management Models
A Complete Guide on Porter Five Forces Model
To recapitulate, the macro environment, external to an organization, has a massive role to play in strategic planning for advancement and expansion. An effective understanding of the macro environment enables organizations to determine the best-fit strategies that are aligned with their strategic goals. This explains why business analysts and consultants give immense importance to the analysis of external business factors that define the macro environment.
FAQs
How can businesses adapt to changes in the macro environment?
Adapting to changes in the macro environment is essential for business survival and growth and it can do so by
Monitoring trends: Stay informed about political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal changes that could impact the business.
Ensuring Flexibility: Build a flexible organizational structure and strategies that can adjust to shifting conditions.
Enabling Diversification: Expand the product or service portfolio to mitigate risks associated with changes in specific industries or markets.
Embracing Innovation: Embrace technological advancements to improve products, services, and operations.
How can businesses conduct a macro environment analysis to inform their strategies?
Business managers can perform a macro environment analysis by conducting a PESTEL analysis that would help them understand various factors such as political, economical, etc., and then gather data to analyze the impact of these factors. Then ultimately, formulate strategies accordingly.
What are the tools used for external analysis of the business environment?
A business manager can make use of PESTEL Analysis to examine the various factors that can influence business operations, and apply SWOT analysis to understand the threats and opportunities from the environment to a business.

 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register