Overview of Nudge Theory
The Nudge Theory, proposed by Cass Sunstein and Richard Thaler in their book "Nudge: Improving Decisions about Health, Wealth, and Happiness" published in 2008, has gained significant recognition as a powerful tool for behavioral economics. Both Sunstein and Thaler are renowned behavioral economists hailing from the United States. The core principle of the Nudge Theory centers around engaging people in the process of change management by understanding how they make decisions and choices.
This theory suggests that subtle actions, known as "nudges," can have a substantial impact on individuals' choices and behaviors. Rather than employing direct instructions or mandates, the Nudge Theory advocates for techniques of indirect influence. The key idea is to respect people's right to make their own choices while gently steering them towards more desirable outcomes. In essence, the theory promotes the use of gentle nudges instead of restrictive measures to drive behavioral change in a positive direction.
Table of Contents
What is Nudge Theory?
Nudge Theory is a concept in behavioral economics that proposes a gentle and indirect approach to influencing people's decisions and behaviors. It recognizes that human beings are susceptible to biases and cognitive limitations, which can affect their decision-making processes. The Nudge Theory aims to leverage this understanding to guide individuals towards making better choices without restricting their freedom of choice.
According to the Nudge Theory, small, strategically designed interventions can significantly impact people's behavior. These interventions are called "nudges" and can take various forms, such as framing information differently, altering the presentation of choices, or providing personalized feedback. Nudges encourage people to make choices aligned with long-term well-being or societal goals, similar to how WordPress web design guides user-friendly decisions.
Application of Nudge Theory for Organizational Change Management
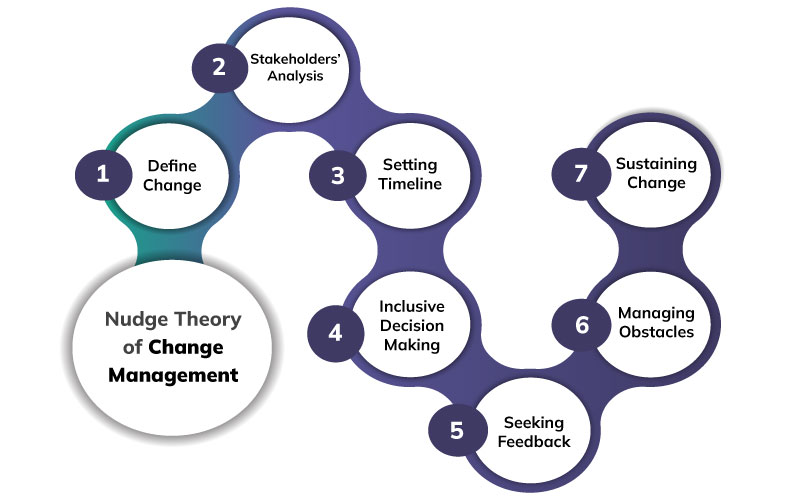
As per the theory, the following steps are essential to successfully implement organizational changes.
- Defining the Change: The first step, as in most change management models, is to define the change by explaining what it aims to achieve and how things will get transformed when the project is successfully completed. The idea of success related to the change has to be visualized and explained to others. While defining the change, it is also essential that change managers define the need for the change, the shared values associated with the change, long-term objectives, and the impact at organizational and individual levels. If the success of the change will be measured using some specific metrics, those metrics need to be defined beforehand too.
- Conducting Stakeholders Analysis: As the Nudge Theory suggests, changes should not be enforced on employees by creating strict norms. Hence, there needs to be a stakeholders analysis to get perspective into how employees view the change and why they are resistant to it. The top management should try and understand employees’ viewpoints without any bias. Stakeholders analysis will help in determining which stakeholders will be directly impacted by the change and also the stakeholders responsible for sustaining the change.
- Creating a Timeline: The change then needs to be planned by associating milestones and a timeline with the project. This is a part of the effective process of planning the change in an efficient way. Milestones need to be set and then further communicated to the people who will be responsible for achieving the milestones. To track if the progress is aligned with the set milestones or not, change managers also need to define the project management KPIs that are going to be used to gauge milestones.
- Keeping Decision Making Inclusive: The change should be presented to employees as a choice and not a mandate. For that, the best way out is to keep the change management process inclusive and hence seek opinions and thoughts from employees. The more inclusive the decision making the greater will be the comfort with the change and the support for it.
- Seek feedback: Change managers and leaders need to be receptive to feedback from their teams with respect to possible shortcomings in planning or the design of the change. As per the Nudging theory, seeking feedback is essential whether it is from employees or even customers. It would be a great strategy to establish strong mechanisms for regular feedback sharing wherein both employees and leaders can share their feedback effectively and constructively.
- Negate Obstacles: Feedback often helps in the identification of issues or obstacles that can affect the success of a change. The next step is to display effective leadership and limit the obstacles and hindrances from affecting the change management process. To negate the obstacles effectively, change managers and leaders might have to replace old systems and processes with new ones. Besides, negating obstacles will also require revamped strategies to motivate and engage employees so that they can overcome the obstacles. Besides, the elimination of obstacles may also require tools and technologies to track things or to resolve problems. The people leading the change should first identify all obstacles in an efficient way and then they need to look for ways to specifically counter each obstacle.
- Maintain Consistency: Nudging theory further explains that consistency in effort and momentum is pivotal to the successful implementation of organizational transformations. Also, the momentum should be sustained with the celebration of milestones that are important to the change process. Change leaders need to present a long-term vision with respect to how they want the change to be a part of business as usual and what is the scope of optimizing its impact in the coming years. At this stage, strategies need to be planned for knowledge sharing, tracking the scalability of the change, fixing accountability for advancing the change, and combining analytics with the transition.
Nudge Theory Change Management example taking Tesla’s case
Tesla as we know is yet to enter the Indian automotive market given the large import duties and other constraints. However, when that happens, it will be a major operational change for the company. Now to successfully implement this project of capturing the Indian market, Tesla can use the Nudge Theory by applying the following processes.
- Defining the change: Tesla can define its success in terms of capturing one of the fastest-growing automotive markets in the world. It can define how the revenue of the company will see major gains after it launches its cars in the Indian market.
- Stakeholders analysis: The top management will have to discuss this project with its lead production engineers, marketing executives, quality engineers, line managers, and board of directors about expanding to the Indian market. Stakeholders will offer their perspectives and expert opinions that will be valuable to the company.
- Setting a timeline: Tesla will further set a timeline in terms of starting its production, operations, and sales in India. Also, different milestones can be set, for instance, the sale of 10000 cars in India within the first year.
- Inclusive decision making: As the Nudge theory suggests, change should be presented as a choice. Having said that, before the details of the project are finalized unilaterally by the top management, Tesla should enact a policy of inclusive decision making if it's going by the Nudge Theory. For instance, it can seek opinions of whether Tesla should locally manufacture in India or not.
- Seek feedback: In the process of this project, Tesla should constantly seek feedback from key stakeholders and department heads. Also, it can take Indian customers’ feedback into consideration to plan its expansion to India and the extent of the same.
- Limiting obstacles: Government clearances, red-tapism in India, less demand for electric cars in India can be some obstacles this ambitious project can face. The company needs to discuss these obstacles and create plans for negating them.
- Maintaining consistency: The momentum should be kept positive and there needs to be consistency in the effort by Tesla’s top management to implement the new project successfully. Tesla can celebrate milestones like getting government approval or mergers with Indian companies to keep the momentum going.
FAQs
Is Nudge Theory manipulation?
Nudge Theory is often criticized for being manipulative, but its proponents argue that nudges are designed to be transparent, ethical, and in the best interest of individuals.
How does Nudge Theory differ from traditional approaches to behavior change?
Unlike traditional approaches that rely on regulations or mandates, Nudge Theory emphasizes gentle, subtle interventions that encourage desirable behaviors through choice architecture.
What are the limitations of the Nudge Theory?
Nudge Theory has certain limitations. Firstly, nudges can lead to unintended outcomes. Secondly, designing effective nudges for diverse populations can be challenging. Lastly, continuous evaluation is crucial to measure the impact and ethical implications of nudges.
Are there any legal or regulatory implications associated with Nudge Theory?
While Nudge Theory focuses on non-coercive and voluntary interventions, there can be legal and ethical considerations to ensure that nudges adhere to individual rights and do not undermine personal freedoms.
Pervious Model
ADKAR ModelNext Model
Bridges’ Transition ModelOverview of the model

 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register