
Introduction
In today’s era of massive competitiveness in the business world and the immense pressure on businesses to outperform their competitors, the strategic business analysis holds great value. This explains why businesses are increasingly investing in hiring top analysts and deploying state-of-the-art business analysis tools.
Table of Contents
Moreover, businesses are now increasingly subscribing to different kinds of strategic planning and analysis models to ensure that they are well aligned to their mission and strategic goals. Here, it is imperative to note that as per the purpose of the intended analysis, different strategic planning models are implemented by business leaders. To explain, companies conduct both external business analysis as well as internal analysis of their capabilities to optimize strategies.
Speaking of internal analysis conducted by organizations to evaluate their competencies, VRIO Analysis is a widely applied strategic analysis model used in the corporate world. This meticulous article explains the VRIO analysis model extensively and offers a perfect guide to conducting the VRIO analysis of a company with effective examples.
What is VRIO Analysis?
To begin with, VRIO is an acronym for Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, and Organized. Speaking of the history of the VRIO Analysis Framework, the model was developed by Jay Barney, a highly acclaimed strategic management professor at the University of Utah.
The analysis model is highly effective for companies when it comes to the evaluation of their internal resources and capabilities. By applying the analysis model, business leaders or analysts can determine if their internal capabilities are valuable, rare, inimitable, and organized. By conducting a successful internal analysis using the VRIO model, companies can get insight into the state of their internal capabilities and resources.
Furthermore, such recognition of internal competencies can help companies understand their competitive advantages. In fact, competitive advantages can either be temporary or sustainable in the long run and the VRIO analysis model gives a clear differentiation between the two classifications. Companies can also identify if there are any areas for improvement they need to work on in case any shortcomings in internal capabilities and resources are realized through the model. All in all, using the model, businesses can constantly track their core competencies and find ways to convert their temporary advantages into sustainable advantages.
To further understand the analysis model and how resources and capabilities are categorized into being valuable, rare, inimitable, and organized, let us delve into the stepwise conduct of the analysis. During the stepwise delineation of the process of conducting the VRIO analysis, you will also comprehensively understand which capabilities and resources qualify to be valuable, rare, inimitable, and organized.
How to conduct an effective VRIO Analysis
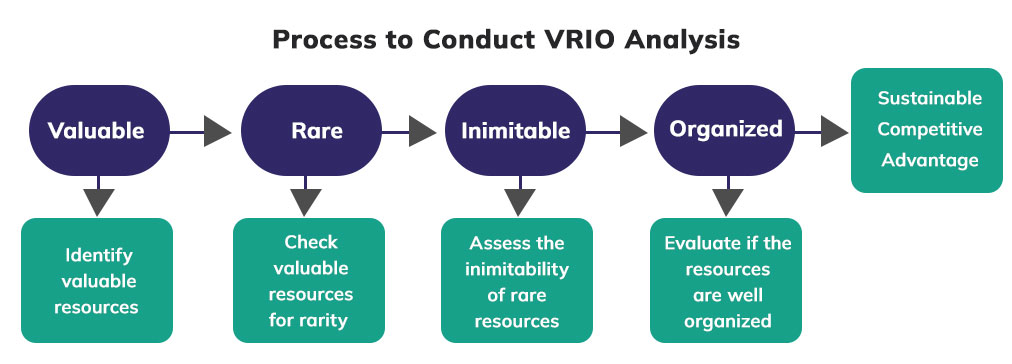
Keen on finding out how a great and conclusive VRIO analysis can be conducted? Let’s get started without further ado.
1. Listing out all the internal resources and capabilities
The first and foremost step in the process of a VRIO analysis is to list down all the internal resources and capabilities. This is a crucial head start with respect to further classifying the resources and capabilities as valuable, rare, inimitable, and organized.
The key is to cover all the internal resources that an organization has and delve deep into the internal capabilities of the organization. Here, you need to be aware of the fact that the model takes into consideration both tangible and intangible resources of a company. You can then arrange all the resources and capabilities in a tabular manner with 4 different columns against them depicting valuable, rare, inimitable, and organized.
Key tip: While conducting a VRIO analysis of a company, you can majorly identify the resources and capabilities of the company through its annual reports. For instance, let’s say you are conducting the VRIO analysis of Toyota. So, you can refer to the annual report of Toyota to assess its financial position and other resources.
2. Identify the resources that are valuable to the company
In the next step, you need to evaluate your list of resources to identify which resources among them are highly valuable to the company. This needs to be looked at in terms of whether a resource adds value to operational efficiency, exploitation of business opportunities, customer acquisition, and so on. If a resource adds great value across these dimensions of internal capabilities, it is identified as valuable.
When the resource identifies as valuable: If the resource is valuable to the company in terms of offer value proposition, in the valuable column, put a tick against the name and move to the evaluation of its rarity.
When the resource does not identify as valuable: In case the resource is not valuable, it is identified as a competitive disadvantage for the company. The company must look to disinvest in the resource or look for immediate measures to make it valuable.
Key tip: High customer loyalty toward a company and massive brand recognition may not be tangible resources but they often identify as highly valuable.
3. Evaluate the rarity of the valuable resources
Furthermore, the next assessment that resources and capabilities need to go through is that of uniqueness. Rare resources and capabilities are those that are unique to an organization and they can certainly play a key role in terms of competitive advantages.
However, evaluating rarity alone is not sufficient here. You also need to look at the resources in terms of demand in the industry or the market. To explain, rare resources are those which are extremely difficult to find elsewhere or with other companies, and at the same time, they also have high demand.
When the resource identifies as rare: When the resources of a company are both valuable and rare, they have great potential of adding to the competitive advantages of the company. For instance, some leadership styles are very rare, and hence, great leaders like Elon Musk are among the most unique resources for organizations. When you identify a resource as rare, you then proceed forward to evaluating its inimitability.
When the resource is not identified as rare: When a resource is valuable but does not qualify for the test of rarity, it only offers competitive parity to a company and not an advantage. Valuable resources that are common do not make it impossible for competitors to pose competitive threats. They only make it challenging for competitors to match up and hence, merely contribute to competitive parity.
Key tip: It will not always be the case that a company’s unique resources cannot be imitated by other competitors. Resources can be rare and still imitable. This is why you further need to check the rare resources for inimitability.
4. Examine the inimitability of resources and capabilities
In this step, you need to ascertain if the resources and capabilities of the company can be duplicated by other competitors or not. In case, resources can be easily duplicated by competitors, they would not qualify as being inimitable. For instance, project management tools, AI integration, IoT sensors in inventory management, and so on can be easily imitated by companies.
When the resource identifies as inimitable: When the resource is inimitable, it has great potential to be a sustainable and long-term advantage for the company. The next step then is to determine if the resource is organized or not.
When the resource does not identify as inimitable: When a resource is unique but can be imitated easily by competitors, it offers a temporary competitive advantage to the company. The fierce competitive rivalry will still exist in the industry as the advantage is only till the time others do not imitate the same resource. For instance, patents are generally valid for around 20 years and after that, companies will lose their temporary competitive advantage when patented technologies or processes will be easy to replicate.
Key tip: Massive R&D investments or a large network of physical stores can be hard for new entrants or small businesses to imitate. For instance, if we look at the R&D investments budget of Apple, it invested USD 21.9 billion in R&D in the year 2021. For most small businesses and medium enterprises, such imitability will not be affordable.
5. Assess if the resources are organized well by the company
This is where capabilities come into the picture primarily. This criterion evaluates if the resources of the company are organized well in terms of processes, management support, company culture, working environment, talent management, and strategic planning. In simple terms, what you need to determine is whether the company has the internal capabilities and structures to get the most out of the available resources.
To conclude, it happens often that organizations have some great resources in terms of brilliant talents, brand recognition, or a massive customer base. However, internal capabilities do not support these resources well. This is exactly what you need to find out and conclude in the last step of the VRIO analysis.
When the resource is well organized: If organizational capabilities extend full support to the resource that is valuable, rare and inimitable, the resource fulfills the criteria of being a sustainable competitive advantage for the company. You can then put a tick in all four columns against the name of the resource.
When the resource is not organized well: If the resource is not backed by organizational capabilities in terms of management support or processes, it counts as an unused competitive advantage. If the resource is valuable, rare as well as inimitable and does not get support from the organizational processes then the company is certainly failing at capitalizing on a readily available competitive advantage.
Now, you have a lucid idea of how you can successfully conduct a VRIO analysis of a company. However, your VRIO analysis should ideally not be limited to putting ticks or crosses against the list of resources with respect to the columns of valuable, rare, inimitable and organized. Your analysis should also explain why you have categorized resources under these categories where they either pass the criterion or fail the criterion.
For a much clearer understanding, we have conducted the VRIO analysis of two real businesses. These examples will help you further polish your comprehension of how the VRIO framework works and how the analysis is presented. So, let us look at the VRIO analysis examples of Apple and Amazon, two of the most successful and renowned businesses in the world.
VRIO
Valuable
Rare
Inimitable
Organized
VRIO Analysis of Apple
With a market capitalization of USD 2.9 trillion, Apple is the world’s most valuable company on the list of the enterprises with the largest market capitalization. Apple today had a leading position when it comes to consumer electronics, software, and web services.
Let us apply the VRIO Analysis Model to Apple to determine how the resources and capabilities of the company make it an industry leader and if there is scope for further enhancements.
| Resources & capabilities | Valuable | Rare | Inimitable | Organized | Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strong financial position | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Temporary competitive advantage |
| Products and services portfolio | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Temporary competitive advantage |
| Innovation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Sustained competitive advantage |
| Global Brand image | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Sustained competitive advantage |
| Company Leadership | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Temporary competitive advantage |
| Intellectual rights and patents | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Sustained competitive advantage |
Apple capabilities and core competencies
As per Apple's financial statement for the first fiscal quarter of 2022, the company reported an all-time high revenue earning of USD 123.9 billion in the quarter. The revenue of the company is up by 11 percent and the cash flow is massive. Even though this resource is not purely inimitable, for most competitors and new entrants, it is very hard to imitate such a financial position. Besides, with such staggering revenue and net income, the company can exorbitantly invest in developing future core competencies. Hence, the company has a temporary competitive advantage in terms of its strong financial position.
Also, the company has a thoughtful and diverse product and services portfolio. From smartphones to wearable technology to laptops, online services, and software, the company’s portfolio is very strong. For new companies or existing competitors, such diversification will be a long as well as expensive process. Hence, the products and services portfolio offers a temporary competitive advantage.
Next, if we talk about the core competencies of Apple, they are enlisted below
- Innovation: Apple has brilliant and futuristic innovation capabilities which are way ahead of contemporary times. Apple’s innovative capabilities and technological infrastructure are highly valuable, rare, and almost impossible to imitate for competitors, especially new entrants. Also, the company is committed to boosting these capabilities and backs continuous research and development. The innovation that consumers get in the form of iOS is in itself a core competency and enables proactive change management.
- Global Brand Image: Apple’s global brand image as a premium smartphone, wearable technology and consumer electronics is almost impossible for other companies to replicate. Apple has always maintained its legacy as a premium brand in global markets and consumers do not feel that any other company can surpass Apple’s reputation. Hence, its global brand image is a core competency. Also, with proactive marketing strategies and aggressive digital marketing tactics, Apple is constantly working on expanding its outreach.
- Intellectual property and patents: Speaking of Apple’s patents, the company has around 72000 patents registered to its name. Even if we say that these patents will lose validity after 20 years, for other companies, imitating these patents would be very costly and development may take years. Hence, the company's intellectual property is its core competency and hence, a sustainable competitive advantage.
- Company leadership: Tim Cook is an exceptional leader who has led the company to remarkable growth. Ever since he took over as the CEO of the company, the market cap of the company grew from USD 364 billion in 2011 to 2.9 billion at present as per CNBC. His innate leadership qualities, vision, and intellect are very hard to replicate. In simple terms, it is almost next to impossible for other companies to find another Tim Cook. Time Cook has proved that he is a core competency in himself for the company and the numbers speaking for it.
VRIO Analysis of Amazon
When was the last time you ordered something from Amazon? For sure, that would have been pretty recent! In the thriving trend of online shopping, Amazon is a globally preferred and beloved brand.
Today, with a market capitalization of USD 1.65 trillion, Amazon is the fifth largest enterprise in the world offering e-commerce, cloud computing, AI, and streaming services to millions of users across the globe. The VRIO Analysis of Amazon will look into the internal resources and capabilities of the organization.
| Resources & capabilities | Valuable | Rare | Inimitable | Organized | Competitive Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strong financial position | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Temporary competitive advantage |
| Products and services portfolio | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Temporary competitive advantage |
| Innovation | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Sustained competitive advantage |
| Global Brand image | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Sustained competitive advantage |
| Company Leadership | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Temporary competitive advantage |
| Intellectual rights and patents | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Sustained competitive advantage |
Amazon capabilities and core competencies
In 2021, Amazon reported its cash flow from operating activities to be USD 46,327 million. For new entrants in the e-commerce industry or the web services industry, having such strong finances will take a lot of years, and still, they may never reach the level at which Amazon operates. Hence, although its financial performance provides a temporary advantage, it is something Amazon can exploit even for decades to come.
Moreover, the global presence of the company and its global operations only provide a competitive parity to the company as most large companies now have a multinational presence. Next, the technological capabilities and innovation of the company offer a temporary competitive advantage. However, for smaller companies or most competitors, it is going to be very expensive to develop technological capabilities at par with Amazon. Also, it will take many years for smaller corporations to reach there and by then Amazon will further step up its technological infrastructure.
Amazon also has impressive diversification strategies in place. It has established itself as the leading e-commerce retailer and it is also bolstering its presence as a streaming service and cloud computing service provider. Since such large scale diversification requires large investments and massive expertise in terms of research and development.
Going further, let us highlight the core competencies of Apple
- Brand Recognition and monopoly control: Amazon is the global favorite when it comes to e-commerce brands and has a leadership position in the global e-commerce retail industry. The company enjoys a monopoly position and as per Statista, Amazon has the largest market share in the global e-commerce retail market. This monopoly control is a core competency of the company and will rather push other industry players to optimize their performance. Amazon has a great understanding of cultural dimensions based on which it has built a leading presence in almost all countries.
- Cost leadership: The company follows a cost leadership pricing strategy and guarantees the lowest prices on almost all products. This cost leadership strategy of the company is its core competency and promotes massive customer acquisition and customer loyalty.
- Company leadership: Jeff Bezos is the founder of Amazon and over the years, he has led his company from being a small online bookstore to the largest e-commerce retailer in the world. His leadership virtues, vision, and intelligible approach are almost impossible for others to emulate. Even if companies go all out in terms of financial spending, finding a leader like Jeff Bezos may still be next to impossible. His leadership style and situational awareness to make the most of opportunities are among the most unique strengths of Amazon.
To conclude, the VRIO Analysis Model is a highly useful and effective tool for internal analysis that can help companies to evaluate their internal resources and capabilities in a holistic way. Subject to this analysis, companies can optimize their strategies and formulate new plans to optimize their resources and capabilities. The effectiveness of this model explains its wide applicability in the contemporary business world.
Recommended Readings
FAQs
What are the limitations of VRIO analysis?
Just like every other framework, VRIO analysis also has a few limitations which are as follows:
- VRIO analysis cannot speculate the future of your values and uniqueness.
- It relies a lot on subjective judgment.
What is the difference between VRIO & Pestle?
VRIO specifically focuses on accessing the internal resources and capabilities of an organization. On the other hand, Pestle is used to access external resources that affect the company’s profitability.

 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register