Overview
WHO (World Health Organization) ranks ischaemic heart disease as the world’s biggest killer and accountable for 16% of the world’s deaths. However, the 21st century has also seen a prevalent condition known as obesity. Obesity isn’t a grievous disease but increases the likelihood of chronic diseases like heart disease, high blood pressure, and stroke, which are the commonest causes of death worldwide. According to WHO, 13% of adults were obese in 2016 and 39% of those aged 18 and above were overweight.
Table of Contents
The organization also reveals that in 2020, 39 million children below the age of 5 were obese or overweight. Additionally, the world’s biggest population lives in countries where obesity and overweight conditions claim more lives than underweight conditions. To substantiate, the World Obesity Federation predicts that over 1 billion people globally will be living with obesity by 2030. Obesity and overweight conditions are considered an epidemic in the modern world and findings indicate that obesity is more common globally than undernutrition. The condition affects both children and adults worldwide, yet adult obesity rates are highest in countries like Nauru, the Cook Islands, Palau, Mexico, and the US. There are different causes of obesity and it can also be looked at as a cosmetic issue.
Handling obesity essays isn’t uncommon for students. If you’re asked to write any topic on obesity, our elucidation on the same can work as a perfect guide for you. This corpus explores the different facets that you may have to consider to present a perfect essay on obesity. Besides, we have added two sample essays in this guide for a more lucid understanding of how you should go about your academic essays on obesity.
However, before we move to the sample essays, let us delve into the aspects of obesity and how it is emerging as one of the most worrisome health conditions in modern times.
Defining obesity
Obesity is a condition where an individual’s weight is higher than what is considered healthy for the age group one belongs to. Those with obesity normally have an excessive amount of body fat. Individuals who are 35 or older with a BMI (body mass index) greater than 30 are considered obese. Being obese or overweight wouldn’t pose an issue, but several findings report that obesity increases the likelihood of serious diseases, like cancer among others.
On the contrary, the CDC stresses that BMI has its limitations when it comes to reflecting obesity in individuals. Factors like age, ethnicity, sex, and muscle mass can all influence the link between body mass index and body fat. Generally, BMI (Body Mass Index) doesn’t differentiate between bone mass, muscle, and excess fat. Yet, it’s widely used to measure body size. One can also have health conditions like Type II diabetes and high blood pressure without being obese.
Types of obesity
Obesity is generally classified into three types, based on severity. These forms of obesity are;
Class I obesity where the BMI is 30 to < 35 kg/m².
Class II obesity where the BMI is 35 to < 40 kg/m².
Class III obesity where the BMI is 40+ kg/m².
If one’s body mass index is between 25.0 and 29.9 kg/m², such a person is categorized as being overweight. Note: Class III obesity was previously known as Morbid obesity.
Now that we have analyzed the types of obesity that are prevalent, the next section sheds light on the peculiar issue of growing childhood obesity.
Childhood obesity
Childhood obesity is a common condition and affects children and adolescents across the top economies of the world. In 2016, WHO estimated that 41 million children below the age of 5 years were obese or overweight. Children or adolescents with obesity have extra pounds and different growth charts may present different BMI averages, depending on the population in question. Childhood obesity is associated with a range of mental, physical, and social issues.
Besides, the projections with respect to the prevalence of global childhood obesity are illustrated in the inforgraphic below
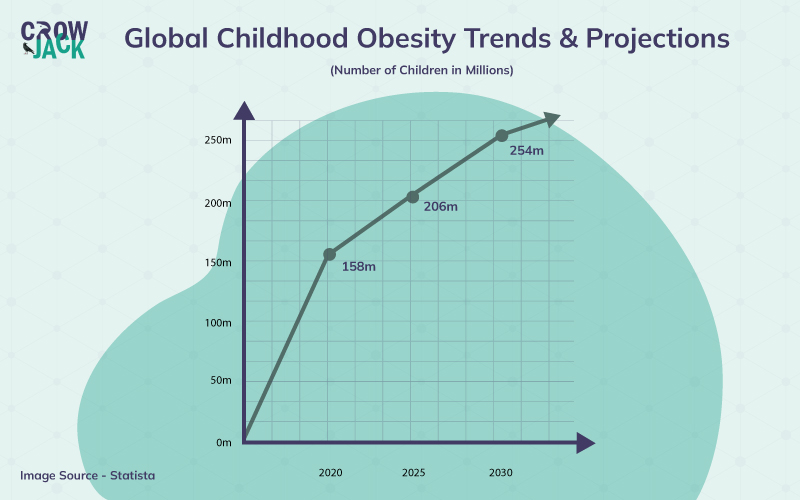
Furthermore, the latest childhood obesity statistics indicate that 39 million children worldwide are obese and WHO estimates that about 167 million people will be less healthy or obese by 2025. However, not all children having extra pounds are obese. For some, it’s largely due to larger-than-average body frames.
Besides, it is also analyzed that the prevalence of childhood obesity is linked with income levels. To substantiate, as per CDC, the obesity prevalence in children was found to be the highest in the middle-income segment (19.9 percent) followed by children in the groups with the lowest income (18.9 percent). Moreover, the obesity prevalence was 10.9 percent in the highest income group.
All in all, childhood obesity has become a major global healthcare concern that requires immediate attention. However, a problem can only be addressed effectively when the causes are recognized. While the most common cause of obesity we often discuss is the massive shift in eating habits among children, there is a lot more to it. Having said that, the next section highlights the major causes of obesity that not only concern children but also adults.
Causes of obesity
There are different causes of obesity in children and adults and the condition is more likely when the body stores a lot of fat. The body may store more fat when there is an imbalance between the number of calories one consumes and those (energy) that the body utilizes. When individuals consume more calories and then live a sedentary lifestyle or engage in less physical activity, it lessens the body’s utilization of the excess calories, resulting in weight gain. That’s why obesity is at times considered a bitter truth of modern lifestyle. There are many causes of obesity in children and adolescents and they include;
1. Genes
Obesity can be a genetic problem running in a family line and several studies have proved this (Choi, Crimmins & Ailshire, 2022).
2. Physical inactivity
Sedentary lifestyles don’t allow people to burn calories or digest their meals effectively. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) shows a huge correlation between physical inactivity and weight gain.
3. Food choices or overeating
Overeating can lead to weight gain and so does junk food. Eating foods high in fat or consuming more sweets, baked products, and fried foods can lead to high-fat-induced obesity or overweight conditions.
4. Hormone imbalances
Hormones control almost every process in the body i.e metabolism, sexual function, mood, sleep, and many of these hormones influence the body’s calorie consumption. For example, the stress hormone cortisol stimulates fat and carbohydrate metabolism. This increases the energy levels in the body, resulting in a bigger appetite. As a result, one will crave more sweet dishes and fatty foods resulting in obesity or weight gain.
5. Medications
Certain medications can trigger weight gain such as antidepressants, anticonvulsants, Tegretol XR, oral contraceptives, etc.
6. Psychological factors
Anger, stress, and frustration can lead to overeating in some individuals which further results in obesity or being overweight. In youngsters, stress eating or emotional eating is a common cause of obesity.
In addition, certain diseases like insulin resistance, PCOS, emotional issues, and exposure to chemicals can lead to obesity in humans.
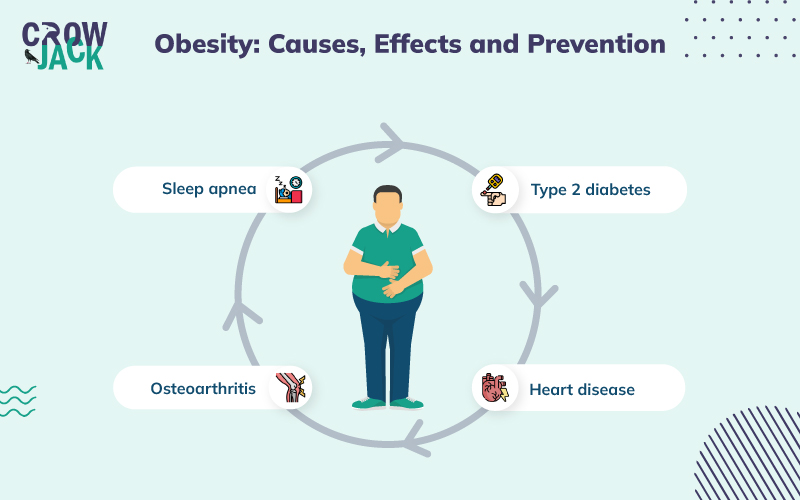
Effects of obesity
Obesity is associated with a range of psychological and social issues. People who are emotionally affected by being obese suffer from low self-esteem, depression, and public stigma. With an overview, all these effects can lead to eating disorders which makes it difficult to treat obesity. On the other hand, obesity increases one’s likelihood of developing serious medical conditions such as heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, gallstones, high blood pressure, breathing issues, and certain forms of cancer.
Children who suffer from obesity are more likely to be bullied by their peers at school or in the neighborhood. Obesity in children also exposes them to several diseases like type 2 diabetes, breathing issues, and cardiovascular diseases. They also have an increased risk of developing low-self esteem later on in life (Mundi et al., 2021).
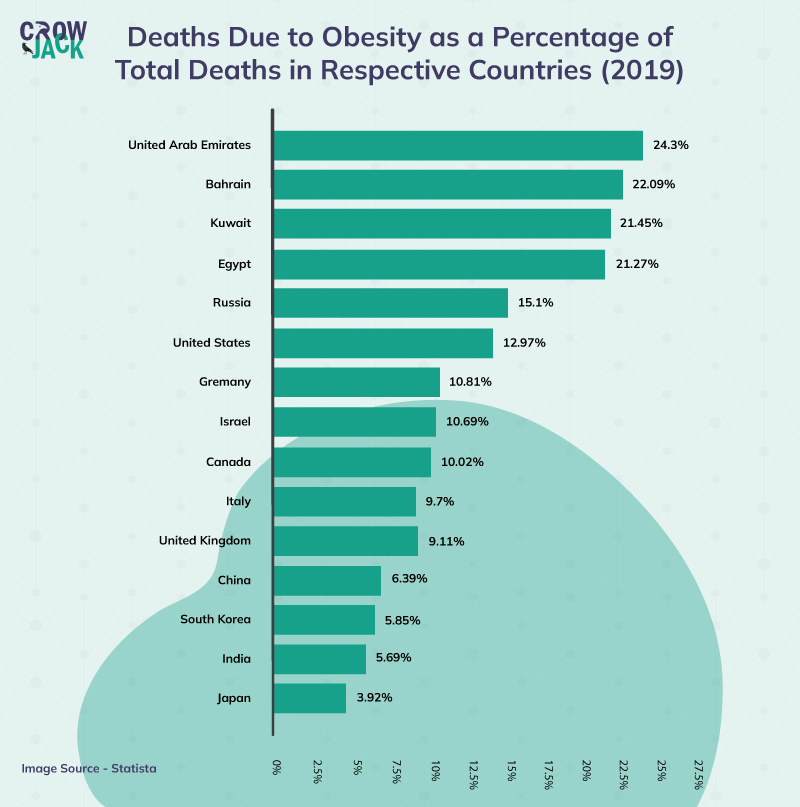
Treatment of obesity
There is a range of obesity treatments i.e surgical and non-surgical, however for one to attain the sought care, treatment must be individualized. Obesity causes differ from one person to another and what might work for person A may not be suitable for person D. For that matter, a personalized diagnosis and treatment approach must be considered to achieve optimal goals.
To diagnose obesity, doctors perform physical examinations or can recommend certain tests. Physical exams include ascertaining one’s BMI, waist circumference, and health history, or taking a general physical exam. The doctor may also request blood tests like a thyroid test, cholesterol test, or liver function test. The results determine a patient’s treatment plan.
In most cases, physical, dietary, and lifestyle changes are recommended for a patient to lose weight. In case they fail to produce desirable results, a patient may opt for surgery. Class III obesity or Morbid obesity is a complex and chronic condition associated with a range of health problems. Treatment options for Morbid obesity include lifestyle changes, medications, behavioral and psychological therapy, and surgical procedures.
Non-surgical obesity treatments primarily include self-improvement measures. These include physical exercise (sports, walking, running), cognitive behavioral therapy, non-fatty foods, and medications like appetite suppressants. Weight-loss surgeries (bariatric procedures) like gastric bypass surgery, endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty, and gastric band surgery can be performed for weight loss.
Sample essays on obesity
Students can take a leaf from the following sample essays on obesity. Also, when you write essays, you need to be aware of the various types of plagiarism to be able to avoid it. Your essay can have a great impression on the readers when it is free from any sort of plagiarism.
Introduction
“Associated with weight gain are increased risks for angina, strokes, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, and premature death”. Besides, treating adult obesity-related ailments costs individuals and governments millions annually. Obesity is one of the principal health concerns of the 21st century in both developed and developing countries. It wouldn’t be seen as a serious issue, but the fact that it is linked to several chronic health conditions such as stroke, heart disease, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cancer, the obesity epidemic remains a significant threat. Obesity ranks as the fifth cause of deaths worldwide (Safaei, Sundararajan, Driss, Boulila & Shapi'i, 2021). Worst still, the condition doesn’t only affect adults, but children and adolescents too. As of March 2022, WHO’s childhood obesity statistics indicated that 39 million children are obese worldwide and the number is certain to increase. This problem solution essay discusses the causes of obesity, its impact, and the possible solutions to tackle its prevalence. For this analysis, different aspects are taken into consideration i.e the notable causes known to be lifestyle factors, the western type of diet, the most affected countries, and a link between COVID-19 and obesity. The first section of the essay defines what obesity is and its causes. The second section puts forth its effects and the possible ways individuals can prevent or treat obesity in the modern era, where lifestyles and work cultures have significantly shifted. The succeeding part then discusses ways individuals can maintain healthy weights across age groups and lifestyles.
Body
The first two paragraphs explain what obesity is and its causes. The details in these paragraphs highly emphasize the food choices in the rural areas and their inability to access health practices as the major cause of obesity. However, the subsequent evidence provides other causes of obesity that cut across regions and individuals despite their status. Obesity is a condition where there is excess fat in the body. Alongside weight gain, it is considered a major lifestyle illness that leads to several chronic health concerns like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (Rychter et al., 2022). Research shows that food insecurity which points to a household’s low ability to purchase healthy food is associated with poor diet and obesity (Choi, Crimmins & Ailshire, 2022). Poor food environments, i.e those with inadequate access to healthy and affordable food increase the likelihood of obesity. Researchers also stress that the frequency and type of food vendors in a region highly determine the kind of food people buy. Fast food restaurants are associated with obesity prevalence. Geographically, some regions present higher BMI cases than others. In the US, the South and the Midwest were found to have the highest levels of adult obesity cases. It was also identified that these regions have a high rate of diabetes and metabolic syndrome, two conditions that usually accompany obesity. Research also found that about 55% of obesity cases can be attributed to the increasing body mass index in rural areas. Rural areas are associated with about 1.3 higher likelihood of obesity compared to urban areas. Rural areas are also known to be farther from clinics, supermarkets, and recreational opportunities which may impact individual and community health practices to prevent obesity.
However, there are many regions and countries with low access to healthy food and have low or no obesity cases and this weakens the earlier argument. There are many other causes of obesity in adults that seem to cut across regions and individuals, whether rich or poor. Other experience-based and evidence-based causes of obesity include genetics, medications, lifestyle-related factors, and neuroendocrine factors like hormonal changes, and hypothalamic disorders (Jiang, Ren, Jiang & Wang, 2021). To a greater extent, obesity is triggered by genes, hormonal imbalances, food choices, lifestyle habits, and other social determinants of health (SDOH). Studies indicate that variants in several genes may contribute to obesity and overweight conditions. A specific variant form is a monogenic obesity. Childhood obesity is largely caused by genes, diet, sleep disorders, overeating, and lack of exercise. In adults, obesity may be triggered by lifestyle, genes, physical inactivity, medications, psychological factors, etc. Causes are largely similar in children, adolescents, and adults.
Further, obesity is associated with a range of physical, psychological, and social effects. To many, obesity is a cosmetic problem, but several studies have shown the aggregated health conditions linked to obesity. The condition affects both children and adults. Obesity also affects the heart, kidneys, liver, joints, and reproductive system. Worldwide, abdominal obesity where excessive fat accumulates around the center of the body is a significant concern among individuals. Many individuals and children who battle obesity have low self-esteem. They usually fail to socialize due to fear of being body shamed. With the fact that such circumstances cause emotional issues, those individuals at times find solace in consuming sweet or junk foods. Junk foods are also poor dietary habits and due to their fat levels, they also double one’s chances of remaining obese. The COVID-19 pandemic also demonstrates how obesity is a public health burden worldwide. Many studies have linked obesity to more severe COVID-19 consequences and mortality. i.e in countries like Brazil (Safaei, Sundararajan, Driss, Boulila & Shapi'i, 2021). Covid-19 patients who are obese have a greater risk of exacerbations from respiratory infections. Patients who were obese were associated with a higher risk of influenza-related ICU and a greater need for mechanical ventilation than non-obese patients during the 2009 swine flu pandemic. A similar case was with the covid-19 patients. Patients with a higher body mass index had an increased risk of breathing problems, longer hospitalization, the need for mechanical ventilation, and death (Albashir, 2020).
However, other health risks associated with obesity include insulin resistance, which is the impaired response or use of insulin by the body system. Obesity is associated with other severe and chronic diseases like cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and high cholesterol which are leading causes of death globally. WHO stresses that obesity is preventable. This means that individuals, families, communities, and nations can take part in reducing or fighting obesity. Children who are also victims of bullying have an increased risk of developing physical and psychosomatic disorders (Bejerot et al., 2022).
Childhood obesity prevention is possible by promoting healthy eating habits in children like increasing the intake of fruits, and healthy proteins and avoiding too many snacks and sweets. Encouraging kids to take part in sports rather than spending a lot of time on hand-held gadgets can reduce childhood obesity. Limiting the consumption of calorie foods can help lower the risk of obesity in individuals (Shatwan & Almoraie, 2022).
Individuals can consider a range of approaches to treat obesity and weight gain. These fall into different categories like surgical and non-surgical approaches. Non-surgical methods like physical exercises, customized diet plans, and weight loss medications are effective in treating obesity (Lee et al., 2022). Regular physical exercise helps the body to burn more calories and cut down the accumulated fats. Physical activity is associated with no side effects like medications or surgery. Besides exercising, meditation can also promote a healthy body and mind by helping individuals cope with stress and other mental disorders. Dieting is effective in stopping further weight gain, however, it must be used realistically. Concerning surgery, individuals opt for it in case other remedies and tips offer no substantial results. Bariatric surgery is a joint name for procedures where changes are made to the digestive system for an individual to lose weight. Undergoing weight-loss surgery requires one to first understand the involved risks and complications (Drillinger, 2022).
Conclusion
Obesity presents a major health challenge worldwide since it highly leads to serious diseases like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Obesity also contributes to serious complications in COVID-19 patients like breathing difficulties. This essay details the definition of obesity, the causes of obesity, childhood obesity prevention, and overall obesity treatment worldwide. The modern era presents a range of approaches individuals can utilize to maintain healthy body weight. Since obesity is highly preventable, individuals must assess the likelihood of developing obesity earlier. Dietary habits, regular exercise, and maintaining an active lifestyle are possible ways to prevent obesity. Attaining professional help whether to prevent or to maintain a healthy body is also recommended.
Liked our sample essay? We are sure you found this essay insightful! To ensure you essays match such quality, you can avail our proofreading services. Our seasoned academic editors are available round the clock to assist you with proofreading.
Introduction
As per the World Health Organization, 39 million children below the age of 5 were obese or overweight in 2020. The prevalence of childhood obesity worldwide is alarming, especially in developing and developed countries like the US. The obesity percentage in America stands at 36%, making it the most obese country among OECD countries. WHO indicates that 39 million children globally are obese and estimates that 167 million adults and children will be less healthy by 2025 because they are overweight or obese. Childhood obesity is associated with a set of physical and psychological factors. Worst still, some children who are overweight or obese during childhood are more likely to stay that way till adulthood. Obesity in children is also linked to several chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease, as in adults. Childhood obesity is triggered by a set of factors that stream from genetic factors, and eating habits, to environmental factors. This essay discusses the different causes of childhood obesity, childhood obesity in America, and how to prevent it. It will throw more light on the greatest contributor to obesity being genes (evidence-based) and other possible causes of childhood obesity like poor eating habits. The subsequent paragraphs shed light on the possible ways to treat and prevent childhood obesity.
Body
Childhood obesity (pediatric obesity) is a condition characterized by excess fat in the body. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicates that childhood obesity prevalence was 19.7% among children and adolescents aged 2-19 years in 2017- 2020. And among those aged 2 to 5 years, the prevalence was 12.7%, whereas it was 22.2% among children aged 12 to 19 years. Not all children who put on extra pounds are obese, but it could indicate obesity if a child reports additional health issues. There are a variety of childhood obesity causes, i.e genes, lifestyle preferences, and cultural and environmental factors. Childhood obesity is prevalent in many countries like China, the US, Brazil, and India. Childhood obesity is highly linked to genes. A scientific study has identified key genes and pathways in childhood obesity. The study investigated the molecular mechanisms involved in childhood obesity by implementing a systems biology approach. To sum it all up, the hub-bottleneck genes were found in cluster 1 and these are suspected to have a significant role in obesity-related pathways (Choi, Crimmins & Ailshire, 2022). Science also terms childhood obesity as a metabolic disorder. An analysis comprising twenty-three studies indicated that children with a high BMI (body mass index) are five times more likely to develop obesity in adulthood than children with a normal weight.
Although genes may prove to be a primary trigger for childhood obesity, other factors like diet, lack of exercise, medications, and psychological factors also play a considerable role. An increase in caloric and fat intake can lead to being overweight. Fast foods, snacks, desserts, baked products, and sugary drinks can trigger obesity in children (Shatwan & Almoraie, 2022). Some children also overeat to cope with stress, fight boredom, or as a way of finding solace. Certain medications like amitriptyline, prednisone, paroxetine, and propranolol can increase a child’s risk of developing obesity. Similarly, a lack of physical exercise where a child spends many hours watching TV, playing mobile games, and eating unhealthy foods increases the risk of obesity.
With childhood obesity, a child normally starts showing extra pounds and may also experience other issues like breathing disorders, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, type 2 diabetes, and sleep apnea. Generally, the condition exposes children to emotional, social, and health issues. They are normally bullied and teased by peers and in the long run, they may also suffer low self-esteem. A study also indicates that childhood abuse is highly linked to obesity, lower-self esteem, and negative experiences with health professionals (Mundi et al., 2021).
Parents and guardians have a huge role to play to prevent childhood obesity. Although sedentary habits like playing video games for considerable hours are known to cause childhood obesity, a certain study proves the effectiveness of mobile health interventions in preventing and treating childhood obesity. Technological advancement is facilitating the development of mobile apps to prevent childhood obesity and some have proved effective (Bonvicini et al., 2022). Parents can also prevent childhood obesity by promoting healthy eating i.e high fiber foods, healthy drinks, and avoiding excess snacking. Curating and following a diet plan can ensure that children attain a substantial balance in nutrients.
Conclusion
All in all, childhood obesity has increased strikingly in recent years. The prevalence of childhood obesity is more in several well-known countries like the US, and China. Obesity in children exposes them to fatal diseases and complications like myocardial infarction among others. Worse still, it is associated with physical, social, and emotional issues. Childhood obesity limits children’s confidence and increases psychological troubles. Eliminating or reducing childhood obesity prevalence requires family, governments, and research intervention to identify more effective solutions. Currently, childhood obesity can be prevented and treated by dietary, lifestyle, physical activity, and medical approaches. Understanding the aggregated impact of obesity on children can help parents design effective approaches to protecting them from obesity. Drawing a clear line between healthy and unhealthy body weights in children and adolescents can also offer better insights to parents about the disease.
References
Safaei, M., Sundararajan, E., Driss, M., Boulila, W., & Shapi'i, A. (2021). A systematic literature review on obesity: Understanding the causes & consequences of obesity and reviewing various machine learning approaches used to predict obesity. Computers In Biology And Medicine, 136, 104754. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104754
Pinhel, M., Watanabe, L., Noronha, N., Junior, W., & Nonino, C. (2021). The intersection between COVID-19 and obesity in the context of an emerging country. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, 44, 472-474. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.005
Choi, Y., Crimmins, E., & Ailshire, J. (2022). Food insecurity, food environments, and disparities in diet quality and obesity in a nationally representative sample of community-dwelling older Americans. Preventive Medicine Reports, 29, 101912. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2022.101912
Choi, Y., Crimmins, E., & Ailshire, J. (2022). Food insecurity, food environments, and disparities in diet quality and obesity in a nationally representative sample of community-dwelling older Americans. Preventive Medicine Reports, 29, 101912. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2022.101912
Bonvicini, L., Pingani, I., Venturelli, F., Patrignani, N., Bassi, M., & Broccoli, S. et al. (2022). Effectiveness of mobile health interventions targeting parents to prevent and treat childhood Obesity: Systematic review. Preventive Medicine Reports, 29, 101940. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2022.101940
Jiang, S., Ren, Q., Jiang, C., & Wang, L. (2021). Academic stress and depression of Chinese adolescents in junior high schools: Moderated mediation model of school burnout and self-esteem. Journal Of Affective Disorders, 295, 384-389. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.08.085
Rychter, A., Hryhorowicz, S., Słomski, R., Dobrowolska, A., & Krela-Kaźmierczak, I. (2022). Antioxidant effects of vitamin E and risk of cardiovascular disease in women with obesity – A narrative review. Clinical Nutrition, 41(7), 1557-1565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2022.04.032
Lee, K., Abraham, S., & Cleaver, R. (2022). A systematic review of licensed weight-loss medications in treating antipsychotic-induced weight gain and obesity in schizophrenia and psychosis. General Hospital Psychiatry, 78, 58-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2022.07.006
Mundi, M., Hurt, R., Phelan, S., Bradley, D., Haller, I., Bauer, K., Bradley, S., Schroeder, D., Clark, M. and Croghan, I., 2021. Associations Between Experience of Early Childhood Trauma and Impact on Obesity Status, Health, as Well as Perceptions of Obesity-Related Health Care. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 96(2), pp.408-419.
Drillinger, M. (2022). Bariatric Surgery Side Effects: What You Should Know. WebMD. Retrieved 26 August 2022, from https://www.webmd.com/connect-to-care/bariatric-surgery/weight-loss-surgery-side-effects.
Mundi, M., Hurt, R., Phelan, S., Bradley, D., Haller, I., Bauer, K., Bradley, S., Schroeder, D., Clark, M. and Croghan, I., 2021. Associations Between Experience of Early Childhood Trauma and Impact on Obesity Status, Health, as Well as Perceptions of Obesity-Related Health Care. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 96(2), pp.408-419.
Drillinger, M. (2022). Bariatric Surgery Side Effects: What You Should Know. WebMD. Retrieved 26 August 2022, from https://www.webmd.com/connect-to-care/bariatric-surgery/weight-loss-surgery-side-effects.
Albashir, A. (2020). The potential impacts of obesity on COVID-19. Clinical Medicine, 20(4), e109-e113. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmed.2020-0239
Bejerot, S., Ståtenhag, L., & Glans, M. (2022). Below average motor skills predict victimization from childhood bullies: A study of adults with ADHD. Journal Of Psychiatric Research, 153, 269-275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.07.019
Shatwan, I., & Almoraie, N. (2022). Correlation between dietary intake and obesity risk factors among healthy adults. Clinical Nutrition Open Science. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutos.2022.08.007

 Proof Reading
Proof Reading  Copy Writing
Copy Writing  Resume Writing
Resume Writing  Blogs
Blogs Guides
Guides SOP's
SOP's Student Resources
Student Resources Research Topics
Research Topics Login
Login Register
Register